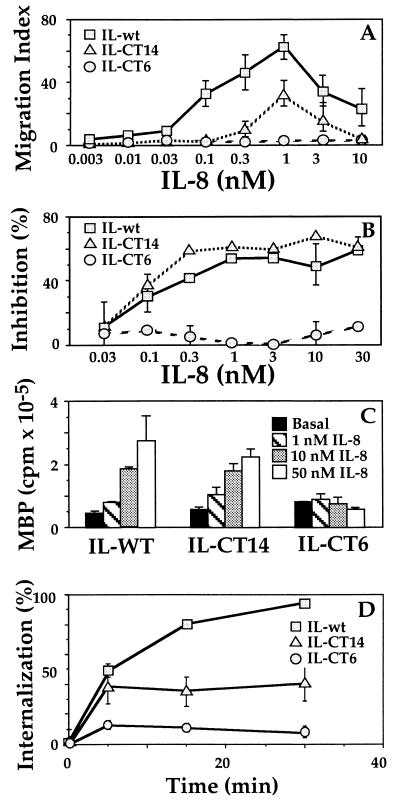
Figure 2.
Wild-type and C-terminal truncation mutants of the IL-8 receptor. (A) Migration assays, performed as described in the legend to Fig. 1, on cells expressing C-terminal truncation mutants (IL-CT14 or IL-CT6) or the wild-type IL-8 receptor (15). (B) cAMP accumulation. Cells were incubated with 200 μM forskolin and the indicated concentrations of IL-8. Values represent percent inhibition by IL-8 of the forskolin-stimulated cAMP response, measured as described (17). Forskolin increased cAMP >100-fold over basal. (C) MAPK (ERK) activation. Stable transfectants were transiently transfected with 1 μg HA-ERK1 DNA and after 48 hr ERK activities were assessed as described (13). ERK activation is expressed in PhosphorImager units. (D) Receptor internalization. The percent of surface receptors remaining after various times of exposure to agonist was measured in whole-cell binding assays using [125I]-IL-8. Data shown represents the mean ± SE of triplicate determinations. Results similar to those in A–D were obtained in three or more independent experiments. HEK293 cell lines expressing the wild-type and mutant IL8Rs were obtained from Adit Ben-Baruch (Tel Aviv University) (15).