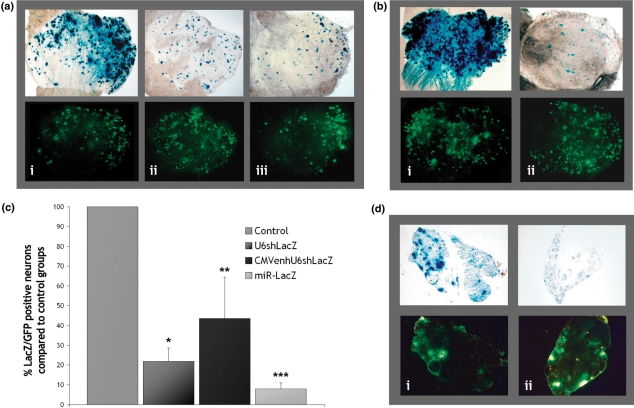
Figure 5.
HSV-mediated silencing in DRG neurons in vivo. (a) BALB/c mice were injected once directly into the sciatic nerve with 1 × 106 plaque forming units (pfu) of a HSV β-galactosidase-expressing vector and 5 × 106 pfu of: (i) the HSV-U6-neg control, (ii) HSV-U6shLacZ, or (iii) HSV-CMVenhU6shLacZ. A GFP-expressing vector was also co-injected (1 × 106 pfu) to monitor transduction efficiency and non-specific silencing. (b) 1 × 106 pfu of a β-galactosidase-expressing vector were injected into the sciatic nerve of BALB/c mice with 5 × 106 pfu of: (i) the HSV-GFP-miR-neg control or (ii) HSV-GFP-miR-LacZ. GFP expression from this system allows labelling of transduced cells and monitoring of non-specific silencing. Silencing was assessed by x-gal staining in whole mount L4 DRG preparations at 7 days post-injection (magnification 5×). (c) Silencing was quantified by directly counting the number of GFP-positive versus β-galactosidase-positive neurons in whole mount DRG preparations (at a magnification 40×). HSV-U6shLacZ reduces β-galactosidase protein levels by 78.0 ± 6.8% (*P = 0.001), HSV-CMVenhU6shLacZ by 62.1 ± 20.9% (**P = 0.02) and HSV-GFP-miR-LacZ by 92.0 ± 3.0% (***P = 0.0002) (n = 3, mean ± SD, results analysed for significance using t-test) (d) Rosa26 transgenic mice were injected into the sciatic nerve with 5 × 106 pfu of: (i) HSV-GFP-miR-neg or (ii) HSV-GFP-miR-LacZ. At 7 days post-injection, the L4 DRG were isolated and sectioned. GFP expressed from these vectors allows simultaneous localization of transduced neurons and monitoring of silencing efficacy. Neurons transduced with HSV-GFP-miR-LacZ are GFP positive and display significantly reduced x-gal staining compared to DRG sections taken from control animals (magnification 10×).