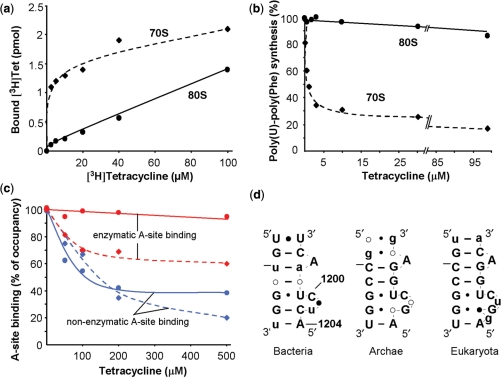
Figure 5.
Analysis of tetracycline binding to 70S and 80S ribosomes. (a) Binding of [3H]Tet to empty 70S (diamonds, dashed line) and 80S (circles, solid line) ribosomes. (b) Poly(U)-poly(Phe) synthesis in bacterial (diamonds, dashed line) and mammalian (circles, solid line) systems in the presence of increasing amounts of tetracycline. The 100% corresponds to 60 and 15 incorporated Phe per ribosome in the bacterial and eukaryotic system, respectively. (c) Effect of tetracycline on non-enzymatic A-site binding with AcPhe-tRNA (blue) and enzymatic A-site binding with ternary complex (red). Deacylated tRNAfMet and  were used to occupy the P site in 70S (dashed line) and 80S systems (solid line), respectively. The 100% corresponds to a ν value of 0.7 for both 70S and 80S ribosomes for non-enzymatic A-site binding and 0.83 and 0.6 for 70S and 80S ribosomes, respectively, for enzymatic A-site binding. (d) Parts of helices 34 from phylogenetic conservation maps superimposed onto the bacterial (E. coli), archaeal (Methanococcus jannaschii) and eukaryotic (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) 16S-type secondary structures (http://www.rna.ccbb.utexas.edu/). ACGU, 98+% conserved positions; acgu, 90–98% conserved positions; filled circle, 80–90% conserved positions; open circle, less than 80% conserved positions. The nucleotides of the right strand are connected for the sake of clarity; number of sequences considered: Bacteria, 4214; Archaea, 174; Eukaryota, 1939.
were used to occupy the P site in 70S (dashed line) and 80S systems (solid line), respectively. The 100% corresponds to a ν value of 0.7 for both 70S and 80S ribosomes for non-enzymatic A-site binding and 0.83 and 0.6 for 70S and 80S ribosomes, respectively, for enzymatic A-site binding. (d) Parts of helices 34 from phylogenetic conservation maps superimposed onto the bacterial (E. coli), archaeal (Methanococcus jannaschii) and eukaryotic (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) 16S-type secondary structures (http://www.rna.ccbb.utexas.edu/). ACGU, 98+% conserved positions; acgu, 90–98% conserved positions; filled circle, 80–90% conserved positions; open circle, less than 80% conserved positions. The nucleotides of the right strand are connected for the sake of clarity; number of sequences considered: Bacteria, 4214; Archaea, 174; Eukaryota, 1939.