Figure 3.
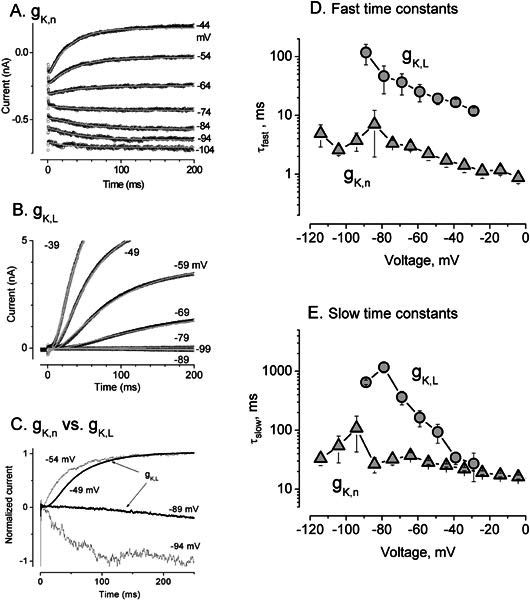
Differences in the activation kinetics of gK,n and gK,L. A,B. Fitting of activation kinetics with Eq.(3) for (A) gK,n from a P16 outer hair cell and (B) gK,L from a P19 type I hair cell. Voltage was first stepped to −124 mV for 500 ms (A) and −129 mV for 200 ms (B) to fully deactivate the conductances, then stepped to the values indicated by each trace. gK,n: V1/2= −87.5, S = 14.1 mV, no second outward rectifier, average of 3 traces at each voltage; gK,L: V1/2 = −83.6, S = 5.0 mV, not averaged. C. Currents from A and B at two similar command voltages, normalized to the current at 3 s for comparison of kinetics. gK,L activated much more slowly at voltages near −90 mV and with a longer delay at voltages near −50 mV. Note that the reversal potentials for these K+ conductances were approximately −80 mV, so that current was inward at −90 mV and outward at −50 mV. D,E. Fast (D) and slow (E) time constants as functions of voltage. Triangles values for gK,n averaged from 5 OHCs. Circles, values for gK,L averaged from 4–5 type I hair cells, except for the data points at −29 mV, which are averages of fits from two cells (τslow = 13.4, 27.2 ms; τfast = 13.4, 11.9ms).
