TABLE 3.
Tecta DNA sequence variations identified in the TectaA349D/A349D mouse
| Exon | Intronic changes | Exonic changes |
|---|---|---|
| −1 | No | No |
| 1 | No | No |
| 2 | No | No |
| 3 | No | No |
| 4 | No | No |
| 5 | IVS5 + 36G > A | No |
| 6 | IVS5−39A > G | 1046C > A (A349D) |
| 7 | No | 1542T > C (T514T) |
| 1713C > T (Y571Y) | ||
| 8 | No | 1893C > T (C631C) |
| 1896G > A (E632E) | ||
| 1944C > T (H648H) | ||
| 2076T > C (S692S) | ||
| 2199C > A (S733S) | ||
| 9 | IVS8−25A > G | 2407T > A (S803T) |
| 2463T > C (G821G) | ||
| 2658T > C (N886N) | ||
| 2691C > T (N897N) | ||
| 2790T > C (V930V) | ||
| 10 | IVS10 + 14G > A | 3094C > A (P1032T) |
| 3366T > C (C1122C) | ||
| 3408C > T (D1136D) | ||
| 3411T > A (S1137S) | ||
| 11 | IVS10−63T > C | 3624T > C (V1208V) |
| IVS11 + 8C > G | 3681T > C (I1227I) | |
| 3685G > A (V1229I) | ||
| 3819A > G (R1273R) | ||
| 3942T > C (C1314C) | ||
| 12 | IVS11−58_59CA > TG | 4149C > T (S1383S) |
| IVS12 + 48C > G | 4260C > T (I1420I) | |
| IVS12 + 82A > G | 4302T > C (Y1434Y) | |
| IVS12 + 92T > C | ||
| IVS12 + 104C > G | ||
| 13 | IVS13 + 50T > C | 4377T > C (C1459C) |
| 4449A > G (K1483K) | ||
| 14 | IVS13−39T > C | 4809T > C (F1603F) |
| 15 | IVS15 + 24T > A | 5028A > G (T1676T) |
| 5106G > A (Q1702Q) | ||
| 5136G > C (P1712P) | ||
| 16 | No | No |
| 17 | IVS16−26G > A | No |
| 18 | IVS17−10T > C | No |
| 19 | IVS18−17A > G | No |
| 20 | IVS19−14T > C | No |
| 21 | No | No |
| 22 | No | No |
| 23 | No | 6442A > G (I2148V) |
All the changes were found in homozygous state and are referred to the genomic Tecta sequence of a wild-type C57BL6J mouse (NT_039472.6). These nucleotide changes, except for the 1046C > A (A349D) mutation, were also found in the ES cell line used to generate the chimeric male transmitting the 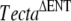 mutation. In addition, we verified that the exonic substitutions accompanying the p.A349D mutation (which include the four amino acid changes p.S803T; p.P1032T; p.V1229I, and p.I2148V) were also present in the Tecta cDNA sequence (NM_009347) of a wild-type CD1 mouse and correspond to single nucleotide polymorphisms.
mutation. In addition, we verified that the exonic substitutions accompanying the p.A349D mutation (which include the four amino acid changes p.S803T; p.P1032T; p.V1229I, and p.I2148V) were also present in the Tecta cDNA sequence (NM_009347) of a wild-type CD1 mouse and correspond to single nucleotide polymorphisms.
IVS Intervening sequence
