Fig. 5.
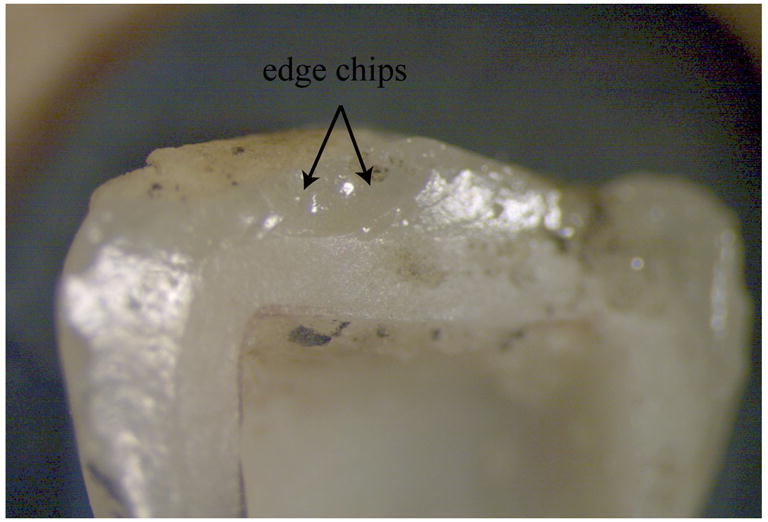


Fig. 5a. Stereomicroscope image focusing on zone 3 showing occlusal surface chip damage.
Figs. 5b,c. SEM images at higher magnifications of zone 3. The veneering ceramic surface has occlusal edge chip damage delimited by arrest lines from which emanate fine twist hackle. The concavity of the arrest lines as well as the river pattern of the twist hackle indicate that the direction of crack propagation (dcp) within the edge chip is running from top to bottom (black arrow).
