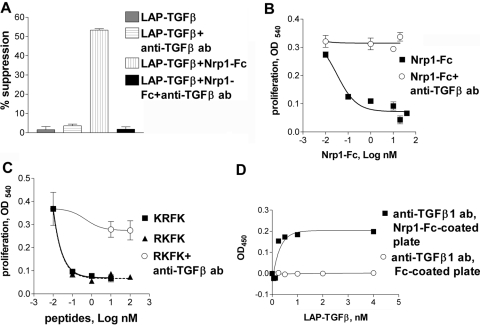
Fig. 4.
Nrp1-Fc and Nrp1 peptides activate LAP-TGF-β1. (A) Soluble Nrp1-Fc (0.4 nM) induced inhibition by LAP-TGF-β1 (0.2 nM) of the proliferation of T cells (CD3 mAb-stimulated), and this was abrogated by the 1D11 anti-TGF-β antibody (50 μg/ml) reactive only to active TGF-β. (B) LAP-TGF-β1 (2 nM) gained the ability to suppress the proliferation of HT-2 cells in the presence of Nrp1-Fc (5 nM), and this was abrogated by 1D11 mAb. In some wells, LAP-TGF-β1 and 1D11 were added without Nrp1-Fc (as a negative control), and as expected, this did not inhibit proliferation (not shown). (C) Nrp1 peptide RKFK and thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) peptide KRFK were equally effective at activating LAP-TGF-β (2 nM), as determined in the HT-2 proliferation assay, and this was blocked by the 1D11 mAb. (D) Binding of LAP-TGF-β1 to immobilized Nrp1-Fc exposed a TGF-β1 epitope recognized by 1D11 mAb.