Fig. 1.
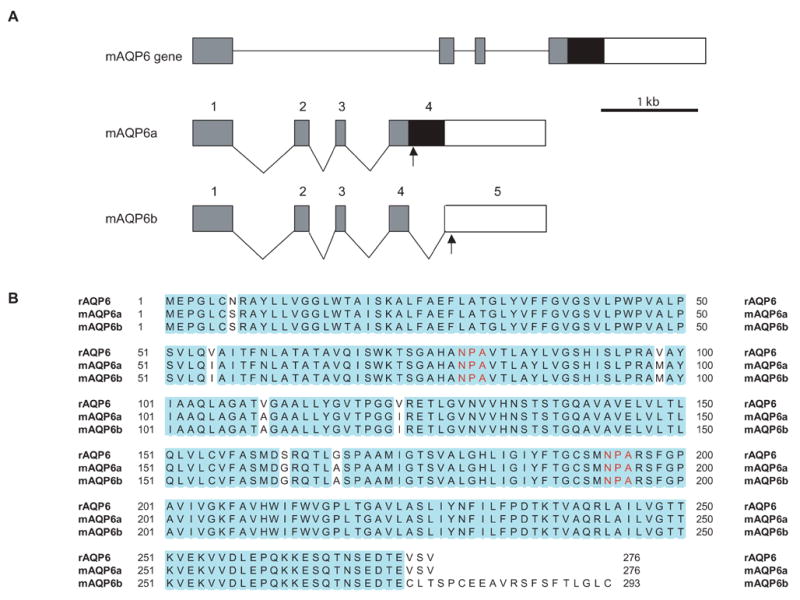
Isolation of mAQP6 splicing variants. A: Exon-intron organization of the mouse AQP6 gene. A segment of the genomic AQP6 clone is shown at the top of the figure. The gray rectangles represent common translated regions of AQP6. Exon 4 of mAQP6a contains a black rectangle with a stop codon in it (arrow). mAQP6b has another intron (intron 4) and exon 5; the stop codon is in exon 5. B: Sequence alignments of rat AQP6, mAQP6a, and mAQP6b. The blue residues are identical. Red ‘NPA’s are a motif of AQPs.
