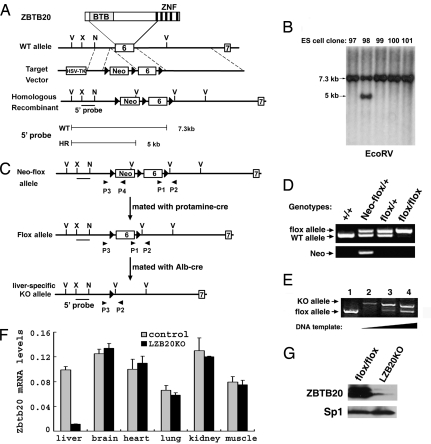
Fig. 1.
Generation of LZB20KO mice. (A) Schematic demonstration for the gene targeting of exon 6 of the ZBTB20 gene. The diagram of ZBTB20 protein is shown at the top. The probe 5′ is used for Southern blot analysis, which detects a 7.3-kb band for the wild-type (WT) allele and a 5-kb band for the homologously recombined (HR) Neo-flox allele in the EcoRV-digested genomic DNA. The loxP sites are represented as filled triangles. V, EcoRV; X, XhoI; N, NcoI; Neo, neomycin resistance cassette. (B) Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones after EcoRV digestion and hybridization with the 5′ probe. Clone number is indicated above each lane. (C) Schematic demonstration for the removal of Neo and tissue-specific deletion of the floxed exon 6 in liver by Cre/loxP-mediated recombination. ZBTB20neo-flox mice were mated with protamine-Cre mice to remove the Neo cassette and produce mice with the ZBTB20flox allele. Repeated mating of ZBTB20flox mice and ALB-Cre transgenic mice generated LZB20KO (ZBTB20flox/flox/Alb-cre) mice. Primers P1 and P2 were used for PCR analysis to confirm the presence of exon 6 and its downstream loxP site, and P3 and P4 were used to detect the Neo cassette. (D) PCR analysis of tail genomic DNA distinguishing the ZBTB20flox allele from the ZBTB20neo-flox and wild-type alleles. PCR with the primers P1 and P2 gave a 0.8-kb band for the floxed allele and a 0.7-kb band for the WT allele (upper row). PCR with primers P3 and P4 produced a 1.0-kb band for the ZBTB20neo-flox allele and no specific band from the ZBTB20flox allele (lower row). Genotypes are indicated above each lane. (E) PCR analysis for Cre-mediated ZBTB20 deletion in liver. Genomic DNA from control (ZBTB20flox/flox, lane 1) or LZB20KO liver (lane 2–4) was subjected to PCR amplification with primers P1, P2, and P3. Deletion of the floxed exon 6 produced a 1.2-kb band amplified by primers P3 and P2, whereas the 0.8-kb band indicates the presence of floxed exon 6. Efficient deletion of the ZBTB20 target exon in liver was shown by PCR products from increasing DNA template inputs (lane 2–4). (F) By real-time PCR, ZBTB20 mRNA expression was shown in control (ZBTB20flox/flox) and LZB20KO mice. (G) Western blot analysis for ZBTB20 protein expression in the adult livers from control (ZBTB20flox/flox) and LZB20KO mice. The nuclear lysate from liver was probed with anti-ZBTB20 (upper row) and anti-Sp1 antibodies (lower row).