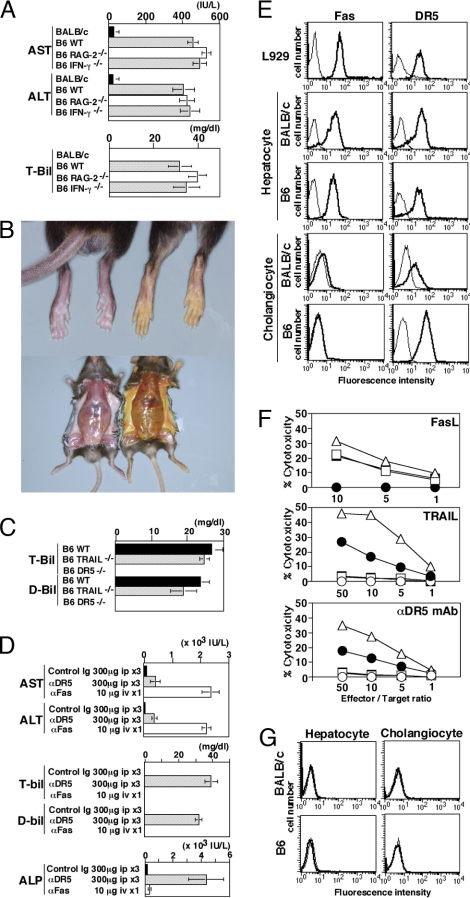
Fig. 1.
Cholestatic liver injury in anti-DR5 mAb-treated B6 mice and sensitivity of cholangiocytes to TRAIL/DR5-induced apoptosis. (A) Serum AST, ALT, and total bilirubin (T-bil) levels of indicated mice treated with intraperitonial injections of anti-DR5 mAb (n = 10 in each group). (B) Jaundice induced by anti-DR5 mAb injections (Right), but not control Ig treatment (Left). (C) Serum T-bil and direct bilirubin (D-bil) levels after anti-DR5 mAb injections in B6 WT, DR5−/−, and TRAIL−/− mice (n = 10 in each group). (D) Serum AST, ALT, T-bil, D-bil, and ALP levels of B6 mice after repeated anti-DR5 mAb or single anti-Fas mAb injection (n = 10 in each group). (E) DR5 and Fas expression on freshly isolated B6 and BALB/c hepatocytes and cholangiocytes. Bold lines indicate the staining with anti-Fas or anti-DR5 mAb; thin lines indicate the staining with isotype-matched control Ig. (F) Sensitivity of L929 cells (triangles) and freshly isolated hepatocytes (squares) and cholangiocytes (circles) from B6 mice (filled circles) or BALB/c mice (open circles) to cytotoxicity by FasL-transfected cells, TRAIL-transfected cells, or anti-DR5 mAb-induced cytotoxicity. (G) TRAIL expression on freshly isolated B6 and BALB/c hepatocytes and cholangiocytes. Bold lines indicate the staining with anti-TRAIL mAb; thin lines indicate the staining with isotype-matched control Ig.