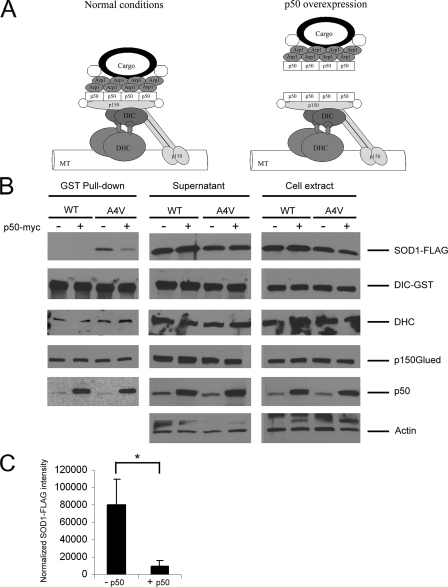
FIGURE 2.
Disruption of the dynein-dynactin complex by p50 overexpression blocks the mutant SOD1-dynein interaction. A, schematic drawing of the dynein-dynactin complex under normal and p50 overexpression conditions. Dynein consists of several subunits including two DHC and two DIC. Dynactin also comprises multiple subunits including eight Arp1, four p50, and two p150Glued. Overexpressed exogenous p50 has been reported to dissociate the cargo binding region from the remaining dynactin complex (42). B, GST pulldowns were performed from HEK293 cells transfected with SOD1-FLAG (WT or A4V), GST-DIC and p50-myc or vector control. Western blotting showed that co-precipitation of A4V mutant SOD1 with DIC-GST was abolished in the presence of p50-Myc overexpression. WT-FLAG did not interact with DIC-GST either in the presence or absence of p50-myc overexpression. DHC and p150Glued were co-precipitated with DIC under all conditions. Overexpression of p50-myc increased the amount of p50 co-precipitated with DIC. C, quantitative analysis from three independent experiments showed an approximately eight times reduction in the amount of A4V SOD1 co-precipitated with DIC in the presence of p50-myc. The band intensity of co-precipitated SOD1 was normalized against that of DIC precipitated. *, p < 0.02.