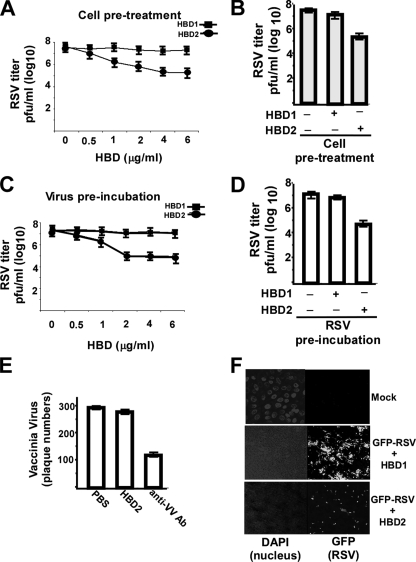
FIGURE 4.
Antiviral activity of HBD2 against RSV infection. A, A549 cells pretreated with either HBD1 or HBD2 (0.5–6 μg/ml) were infected with RSV (in the absence of HBDs) and at 36 h post-infection, and viral titer was measured by plaque assay analysis. B, bar graph showing significant reduction in RSV infection following pretreatment of cells with 4 μg/ml HBD2. C, RSV virion particles preincubated with either HBD1 or HBD2 (0.5–6 μg/ml) were used to infect A549 cells (in the absence of HBDs), and at 36 h post-infection, viral titer was measured by plaque assay analysis. D, bar graph showing significant reduction in infection of A549 cells with RSV preincubated with 2 μg/ml HBD2. The plaque assay values for RSV are expressed as pfu/ml, and each value represents the mean ± S.D. for three determinations. E, vaccinia virus incubated with either PBS (control), HBD2 (10 μg/ml), or neutralizing antibody against vaccinia virus (anti-VV Ab) was used to infect Vero cells, and the plaque numbers were counted at 36 h post-infection. Vaccinia virus infection is represented by the number of plaques, and each value represents the mean ± S.D. for three determinations. F, A549 cells pretreated with either HBD1 or HBD2 (4 μg/ml) were infected (in the absence of HBDs) with RSV expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP-RSV), and at 24 h post-infection, virus infection was monitored by visualizing GFP expression. DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.