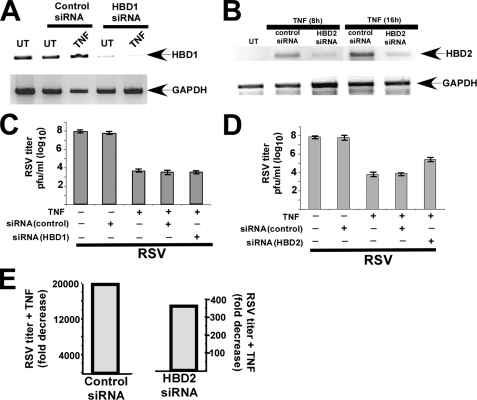
FIGURE 7.
Role of HBD2 in innate antiviral function of TNF. A, total RNA collected from either untreated (UT) or TNF-treated (10 ng/ml TNF treatment for 16 h) A549 cells transfected with either control or HBD1-specific siRNA were subjected to RT-PCR to detect HBD1 and GAPDH (loading control). B, total RNA collected from untreated (UT) and TNF-treated (10 ng/ml TNF treatment for 8 or 16 h) A549 cells transfected with either control or HBD2-specific siRNA were subjected to RT-PCR to detect HBD2 and GAPDH. C, A549 cells transfected with either control or HBD1-specific siRNAs were pretreated with TNF (20 ng/ml) for 20 h, followed by RSV infection for 36 h. Viral titer at 36 h post-infection was measured by plaque assay analysis. D, A549 cells transfected with either control or HBD2-specific siRNA were pretreated with TNF (20 ng/ml) for 20 h, followed by RSV infection for 36 h. Viral titer at 36 h post-infection was measured by plaque assay analysis. E, plaque assay values from D were tabulated to demonstrate the antiviral efficiency of TNF in control and HBD2-silenced cells. The values are represented as fold decrease in viral titer following treatment of control and HBD2-silenced cells with TNF. The plaque assay values for the above experiments are expressed as pfu/ml, and each value represents the mean ± S.D. for three determinations.