Figure 2.
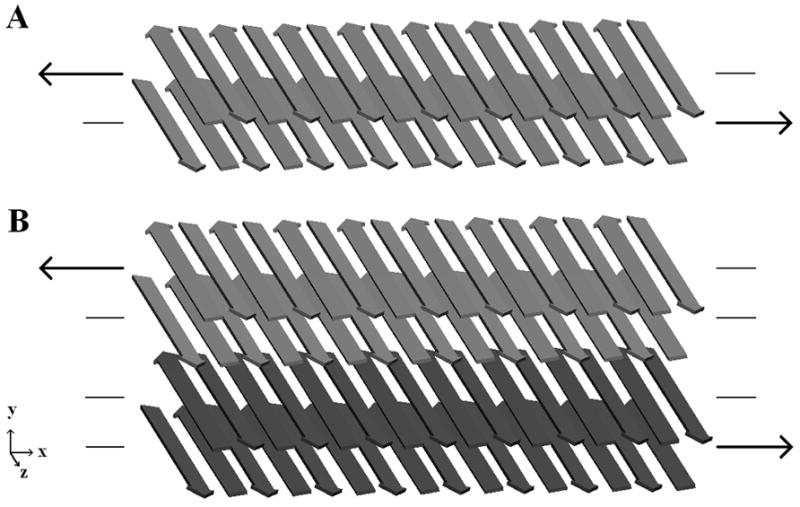
Shear loading schemes for one (A) or two (B) double-layered filaments are shown. (A) Shear stress is applied over the hydrophobic surface at the core of a single filament. (B) Shear stress is applied over the hydrophobic core of each filament and the charged surface between the filaments. In each case a constant force is applied to the α-carbons in one β-sheet, and an opposite force to the α-carbons of another β-sheet. Forces are directed along the filament axis.
