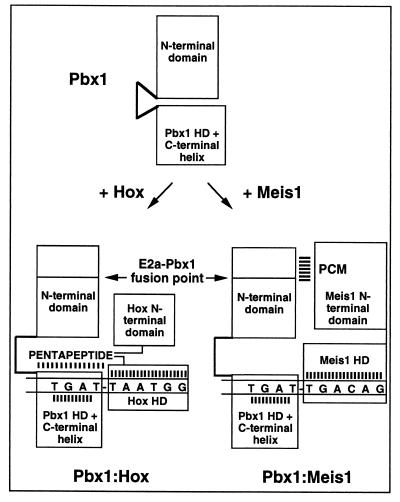
Figure 5.
Model for differential DNA binding by Pbx1–Hox and Pbx1–Meis1 heterodimers. Monomeric Pbx1 contains an N-terminal domain preventing DNA binding by the HD. The monomeric configuration is indicated by the closed-hinge conformation. Dimerization with Hox proteins converts Pbx1 to the open DNA-binding conformation, requiring contact of the Hox pentapeptide with the Pbx1 HD/C-terminal helix domain. Dimerization with Meis1 is proposed to convert Pbx1 to the open DNA-binding conformation through contacts between Pbx1 sequences removed by translocation with E2a and Meis1 sequences that include the M2 Pbx1 cooperativity motif.