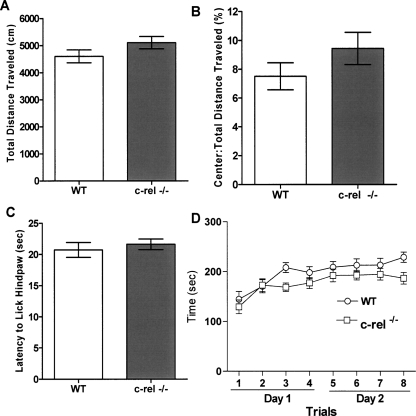
Figure 3.
Basal behavioral characterization of c-rel−/− mice. Several behavioral tasks were performed in both c-rel−/− and wild-type littermate mice to measure their overall levels of locomotor activity, anxiety, nociception, and motor learning. (A) c-rel−/− mice have similar levels of locomotor activity relative to wild-type littermates as assessed by total distance traveled during a 15 min session in the open field task. n = 25 wild-type (14 male, 11 female) and 27 c-rel−/− (18 male, nine female). (B) c-rel−/− mice have similar levels of basal anxiety relative to wild-type littermate as assessed by the ratio of the center:total distance traveled in the open field task. n = 25 wild-type (14 male, 11 female) and 27 c-rel−/− (18 male, nine female). (C) No significant difference was seen in thermal sensitivity between c-rel−/− and wild-type littermates, indicating that nociception is comparable between the two groups of mice. n = 25 wild-type (14 male, 11 female) and 27 c-rel−/− (18 male, nine female). (D) Motor learning of c-rel−/− mice was measured using an accelerating rotarod test. In this test, c-rel−/− mice did not show motor learning deficits compared with wild-type littermates. n = 18 wild-type (11 male, seven female) and 20 c-rel−/− (13 male, seven female).