Figure 8.
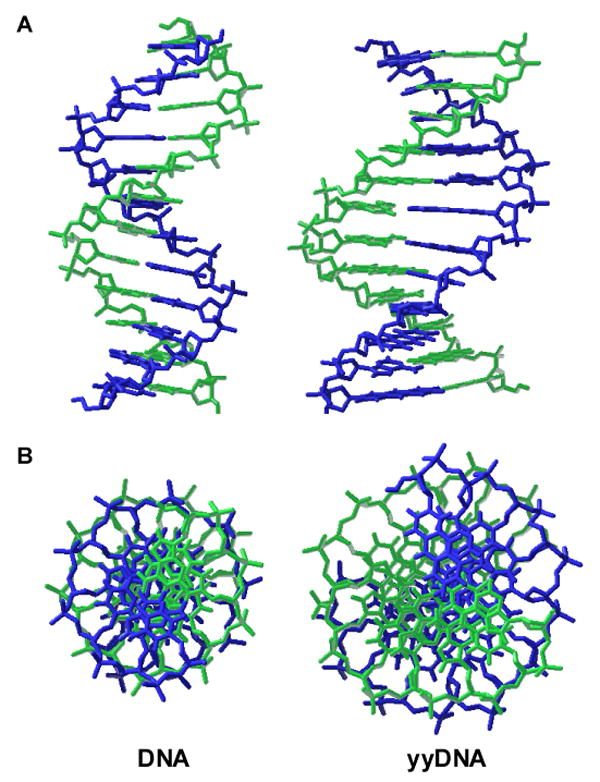
Molecular models comparing natural B-form DNA dodecamer (left) with a plausible model of yyDNA composed of yyT-A and yyC-G pairs (right). Side views (A) and end views (B) are shown. Both modeled structures (AMBER force field; continuum water) are right-handed and antiparallel double helices, with similar sugar conformations. The chief differences predicted for yyDNA are widened grooves and a lower degree of twisting, resulting in ca. 14 base pairs per 360° turn of the helix.
