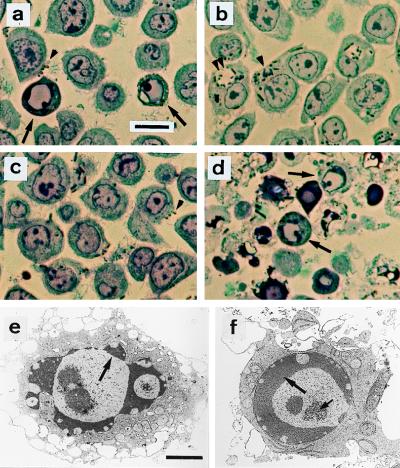
Figure 5.
Structural evidence for Y. enterocolitica-induced apoptosis. Semi-thin sections were stained with toluidine blue and examined by light microscopy (a–d). (a) Wild-type strain E40; apoptotic nuclei (arrows) and cell surface-associated bacteria (brown particles, arrowhead). (b) yscN secretion mutant; no apoptotic cells are detected. Abundance of internalized bacteria either in tight (single arrowhead) or spacious phagosomes (double arrowhead). (c) yopP effector mutant; no apoptotic cells are detected. Bacteria at the cell surface (arrowhead). (d) yopP+++, apoptotic cells (arrows). Ultrastructural analysis of cells infected with yopP+++ from d is shown in e and f. Typical features of apoptosis include (i) peripheral chromatin condensation in crescents, except in the vicinity of nuclear pores (large arrows); (ii) bulging of nuclear crescents into the cytoplasm, best seen in e; and (iii) appearance of central clusters of small particles of unknown nature, typical of apoptosis (small arrow at f). Nuclear and plasma membrane alterations contrast with a good ultrastructural preservation of cytoplasm, particularly of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. (a–d, Bar = 10 μm; e–f, Bar = 2 μm).