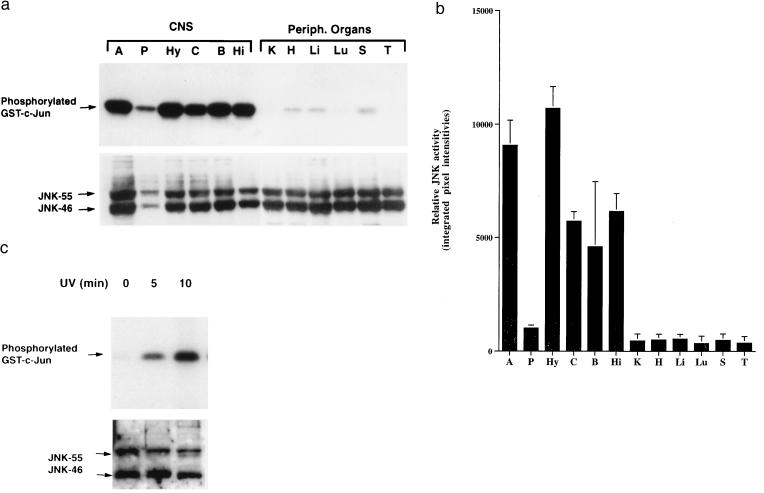
Figure 1.
High levels of JNK activity in the CNS. (a) Representative autoradiograph demonstrating substantially higher basal levels of JNK activity (Upper) in different brain regions [amygdala (A), pituitary (P), hypothalamus (Hy), neocortex (C), brainstem (B), and hippocampus (Hi)] than in peripheral organs [kidney (K), heart (H), liver (Li), lung (Lu), spleen (S), and thymus (T)]. JNK protein levels (Lower) in brain regions and peripheral organs revealed by Western blot analysis. (b) Semiquantitative comparison of JNK activities in CNS regions and peripheral organs. Signals from gels such as the one shown in a were quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis essentially as described (21). Each bar represents the mean JNK activity (error bars SD) identified in three mice in the same kinase assay. Similar results were obtained in two additional independent kinase assays. (c) JNK activation in Neuro-2a cells irradiated with UV-C for 0, 5, or 10 min. Whole-cell lysates were used for JNK enzymatic assay (Upper) and Western blot analysis (Lower).