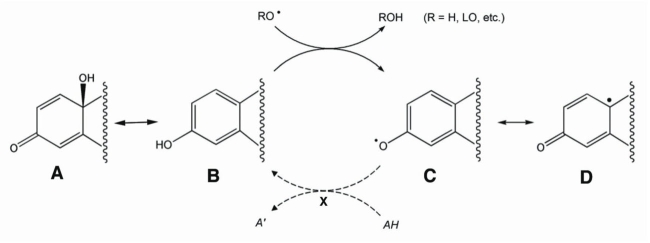
Figure 1.
Termination, stabilization, and recycling of free-radical by phenolic estrogen derived drugs. Structure A represents the quinolic ring that can spontaneously convert to a phenolic ring found in the structure of estrogens. The phenol (B) can then scavenge free radicals (C) and resonance-stabilize them (C-D) until reduced (X). Reduction of phenoxy radicals (C) is an enzyme-mediated process that uses ascorbic acid, glutathione-dependent free radical reductase, and a newly discovered NADPH-mediated reductive aromatization. This illustration was loosely based on work of Prokai et al. [79].