FIGURE 2.
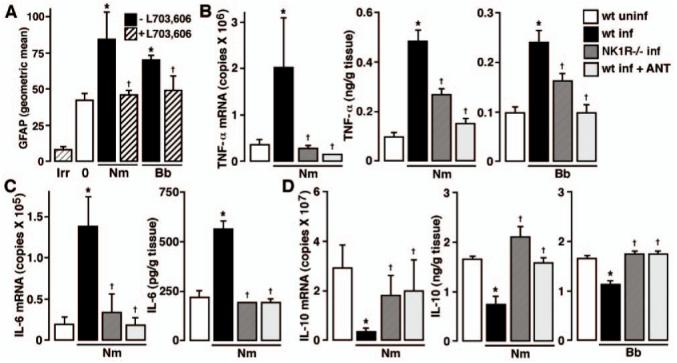
In vivo astrogliosis and inflammatory cytokine production are markedly reduced in the absence of endogenous SP/NK-1R interactions. A, Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were given vehicle or infected with N. meningitidis (Nm) or B. burgdorferi (Bb) (1 × 106) via i.c. injection and were untreated or received s.c. administration of the NK-1R antagonist l-703,606 (5 mg/kg) at days -1, 0, and +1 relative to bacterial challenge. At 72 h postinfection, glial cells were isolated, permeabilized, and GFAP expression determined by flow cytometry. n = 6; Asterisk indicates significant difference from uninfected (0) animals, and dagger indicates significant difference from infected animals that did not receive the NK-1R antagonist. Fluorescence signal obtained using an isotype and species matched Ab directed against an irrelevant Ag is indicated (Irr). B-D, N. meningitidis (1 × 106) (Nm) or B. burgdorferi (1 × 106) (Bb) was administered via i.c. injection into C57BL/6 wild-type (wt) or NK-1R-deficient (NK1R-/-) mice. In addition, groups of wild-type mice received s.c. injections (5 mg/kg) of the NK-1R antagonist l-703,606 at days -1, 0, and +1 to bacterial challenge (wt inf + ANT). At 72 h postinfection, mRNA or tissue homogenates were isolated for measurement of TNF-α (B), IL-6 (C), and IL-10 (D) mRNA and protein expression by real-time PCR and specific capture ELISA, respectively. n = 8; Asterisk indicates significant difference from uninfected (wt uninf) animals, and dagger indicates significant difference from infected wild-type animals (wt inf).
