Fig. 8.
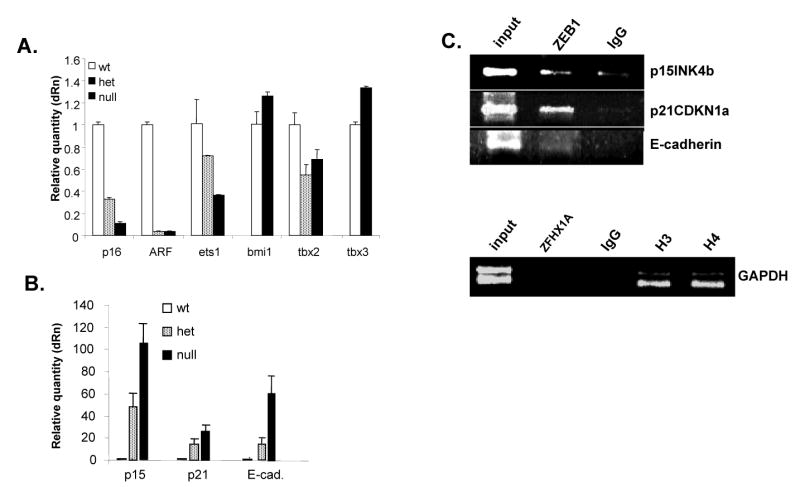
Mutation of the ZEB1 gene does not trigger the classic INK4A replicative senescence pathway in MEFs, instead it is associated with induction of p15INK4b and p21CDKN1a. A. Real-time PCR was used to compare mRNA expression from the INK4a locus (p16INK4a and ARF), and genes know to regulate the INK4a locus, in proliferating wild-type MEFs (P3) and senescent ZEB1 gene heterozygous (P5) and null (P2) cells. B. p15INK4b, p21CDKN1A and E-cadherin mRNAs are induced in a gene dosage-dependent fashion in ZEB1 gene mutant MEFs. Real-time PCR results using the same samples in panel A are shown. C. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. “input” indicates starting chromatin used for the immunoprecipitations; “IgG” indicates pre-immune serum. Histone H3 and H4 are positive controls for the GAPDH promoter.
