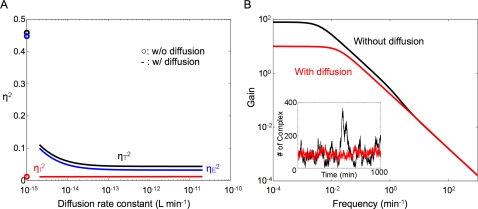
Figure 2. Diffusion reduces the output noise by reducing the extrinsic noise component.
(A) Diffusion drastically reduces the total noise (black) by primarily attenuating the extrinsic noise (blue) without significantly affecting the intrinsic noise (red). Circles represent levels of total (black), extrinsic (blue) and intrinsic (red) noise without diffusion. (B) Diffusion significantly reduces the gain of the low-frequency extrinsic noise components transmitted to the complex. P = 2×10−13 L min−1 for the with-diffusion case. Inset: The corresponding time courses of the complex without diffusion (black) and with diffusion (red). Numerical simulation is implemented using the fixed time step 4th order Runge-Kutta method [56] for the deterministic terms and Euler-Maruyama method for the stochastic terms.