Abstract
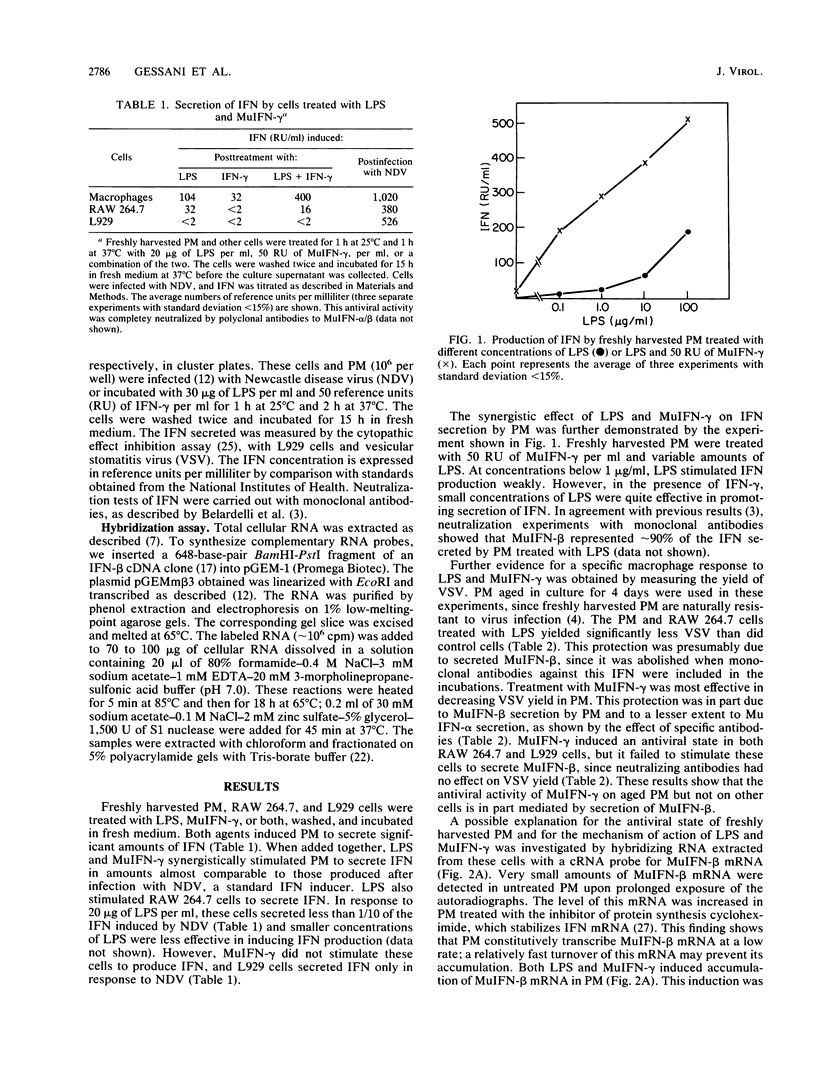
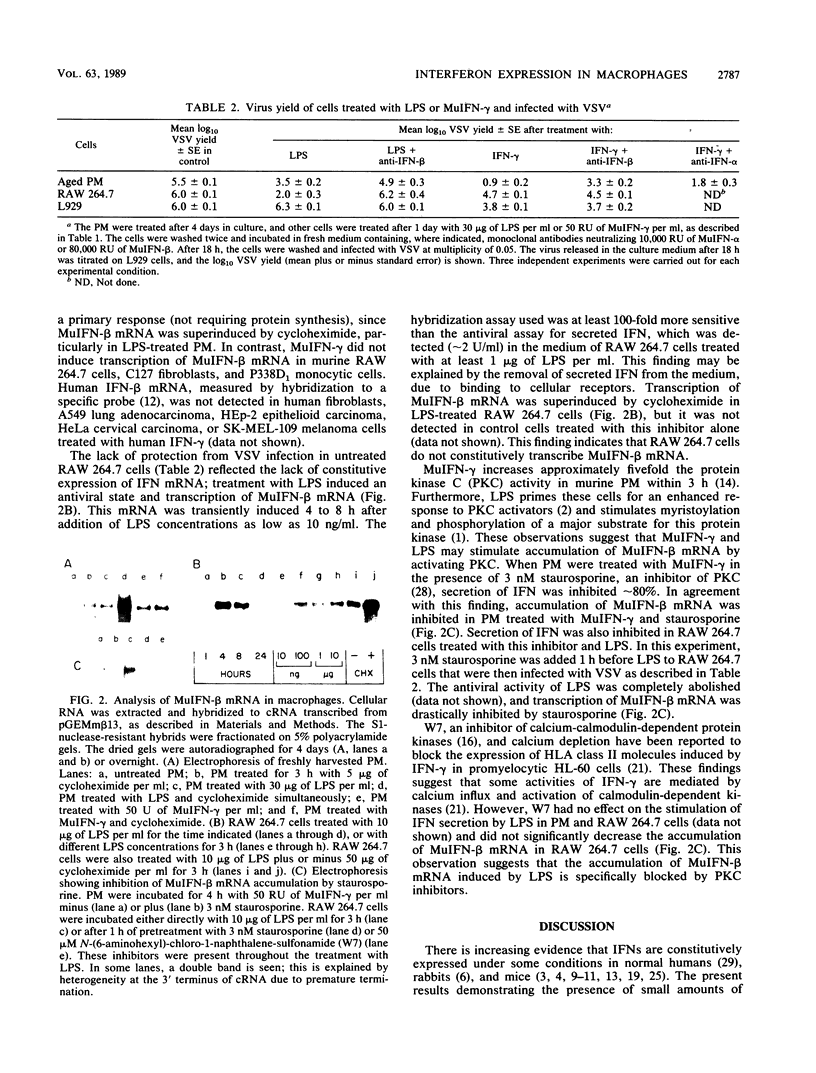
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces interferon (IFN) secretion and an antiviral state in murine peritoneal macrophages (PM). These cells secrete predominantly IFN-beta, as shown by neutralization assays with monoclonal antibodies. Secretion of IFN-beta is also induced in PM by IFN-gamma. LPS and IFN-gamma synergistically stimulated PM to produce IFN in amounts almost comparable to those induced by infection with Newcastle disease virus. Low levels of IFN-beta mRNA can be detected in freshly harvested PM by hybridization assays. The accumulation of this mRNA is markedly increased in PM treated with LPS or IFN-gamma, and it is further enhanced in the presence of the inhibitor of protein synthesis, cycloheximide. Similar studies were carried out on the RAW 264.7 line of transformed macrophages. These cells are induced to secrete IFN-beta by LPS but not by IFN-gamma, suggesting that this cytokine may elicit such specific response only in PM. IFN-beta mRNA is undetectable in untreated RAW 264.7 cells, and accumulation of this mRNA is induced by LPS but not by IFN-gamma. The secretion of IFN induced by these agents in PM and by LPS in RAW 264.7 cells and the corresponding accumulation of IFN-beta mRNA are blocked by an inhibitor of protein kinase C, staurosporine. The activity of this kinase is apparently necessary to stimulate accumulation of IFN-beta mRNA. The induction of IFN-beta by IFN-gamma appears to be a characteristic response of PM and may be at least in part responsible for the resistance of these cells to viral infections.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderem A. A., Albert K. A., Keum M. M., Wang J. K., Greengard P., Cohn Z. A. Stimulus-dependent myristoylation of a major substrate for protein kinase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):362–364. doi: 10.1038/332362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aderem A. A., Cohen D. S., Wright S. D., Cohn Z. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides prime macrophages for enhanced release of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belardelli F., Gessani S., Proietti E., Locardi C., Borghi P., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Gresser I. Studies on the expression of spontaneous and induced interferons in mouse peritoneal macrophages by means of monoclonal antibodies to mouse interferons. J Gen Virol. 1987 Aug;68(Pt 8):2203–2212. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-8-2203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belardelli F., Vignaux F., Proietti E., Gresser I. Injection of mice with antibody to interferon renders peritoneal macrophages permissive for vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):602–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocci V., Muscettola M., Paulesu L., Grasso G. The physiological interferon response. II. Interferon is present in lymph but not in plasma of healthy rabbits. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):101–108. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Robert N., Buffet-Janvresse C., Rivière Y., Hovanessian A. G. Continuous production of interferon in normal mice: effect of anti-interferon globulin, sex, age, strain and environment on the levels of 2-5A synthetase and p67K kinase. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):711–718. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., Belardelli F., Borghi P., Boraschi D., Gresser I. Correlation between the lipopolysaccharide response of mice and the capacity of mouse peritoneal cells to transfer an antiviral state. Role of endogenous interferon. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1991–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., McCandless S., Baglioni C. The glucocorticoid dexamethasone inhibits synthesis of interferon by decreasing the level of its mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7454–7457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Vignaux F., Belardelli F., Tovey M. G., Maunoury M. T. Injection of mice with antibody to mouse interferon alpha/beta decreases the level of 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase in peritoneal macrophages. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):221–227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.221-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Becton D. L., Somers S. D., Gray P. W., Adams D. O. Interferon-gamma modulates protein kinase C activity in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1378–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Spitalny G. L. Endotoxin-induced interferon synthesis in macrophage cultures. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 May;33(5):369–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Sasaki Y., Tanaka T., Endo T., Ohno S., Fujii Y., Nagata T. N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide, a calmodulin antagonist, inhibits cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4354–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes T. K., Baron S. A large component of the antiviral activity of mouse interferon-gamma may be due to its induction of interferon-alpha. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1987 Jan-Mar;1(1):29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Aoki H., Kimura Y., Takano M., Shimokata K., Maeno K. Natural interferon-producing cells in mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):519–523. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.519-523.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification of an inducible factor that binds to a positive regulatory element of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3309–3313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide Y., Ina Y., Nezu N., Yoshida T. O. Calcium influx and the Ca2+-calmodulin complex are involved in interferon-gamma-induced expression of HLA class II molecules on HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3120–3124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen S. C. Role of macrophages in natural resistance to virus infections. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):1–26. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.1-26.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proietti E., Gessani S., Belardelli F., Gresser I. Mouse peritoneal cells confer an antiviral state on mouse cell monolayers: role of interferon. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):456–463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.456-463.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C., Baird S., Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Functional macrophage cell lines transformed by Abelson leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Lyles D. S., Tamm I. Superinduction of human fibroblast interferon production: further evidence for increased stability of interferon mRNA. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):186–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Streuli M., Gresser I., Gugenheim J., Blanchard B., Guymarho J., Vignaux F., Gigou M. Interferon messenger RNA is produced constitutively in the organs of normal individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5038–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Fertsch D. Macrophages from endotoxin-hyporesponsive (Lpsd) C3H/HeJ mice are permissive for vesicular stomatitis virus because of reduced levels of endogenous interferon: possible mechanism for natural resistance to virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):812–818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.812-818.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., Fauve R. M., de Maeyer-Guignard J. Production d'interféron au niveau du macrophage. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Mar;120(3):438–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



