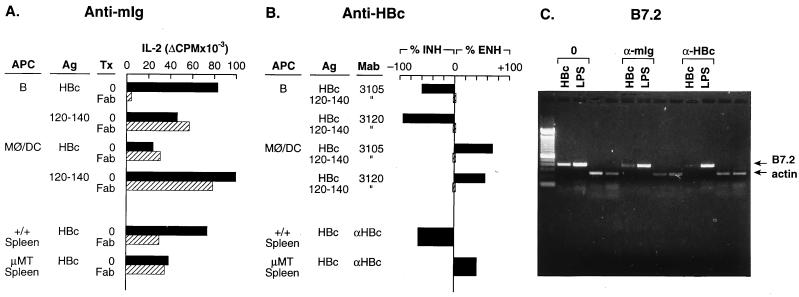
Figure 3.
B cell presentation of HBcAg and B cell B7.2 mRNA induction by HBcAg are mediated through HBcAg-specific mIg receptors. B cell APC were prepared from unprimed B10 (H-2b) mouse spleen, as were non-B cell APC (i.e., MØ/DC) by the methods described. (A) Inhibition of APC–T hybridoma activation by anti-mIg. Unprimed, B cell APC (2 × 105) were cultured with HBcAg (1.0 μg/ml) or peptide 120–140 (2.5 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of goat anti-mIg Fab fragments (25 μg/ml) or goat Ig (25 μg/ml) for 1 h before the addition of 1.2 × 104 IAb-restricted, HBcAg-specific T hybridoma (7B7–1A12) cells. MØ/DC APC (2 × 105) were cultured with a 10-fold-higher concentration of HBcAg (10 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of Fab anti-mIg 1 h before the addition of the 7B7–1A12 T hybridoma cells. The APC–T hybridoma cells were cultured for 16 h, and SN was collected for determination of IL-2 production. Assays were also performed by using either unprimed +/+ B6 spleen cells (1.0 μg of HBcAg) or μMT spleen cells (10 μg/ml of HBcAg) as the source of APC. (B) Inhibition of APC–T hybridoma activation by anti-HBc antibodies. Unprimed, B cell APC (2 × 105) were “pulsed” with HBcAg (1.0 μg/ml) or 120–140 (2.5 μg/ml) for 30 min in the presence or absence of anti-HBc mAb 3105 (5 μg/ml) or mAb 3120 (5 μg/ml), washed, and then cultured with HBcAg-specific T hybridoma 7B7–1A12 cells (1.2 × 104) for 16 h, and SN were harvested for IL-2 measurement. MØ/DC APC were cultured similarly, but were “pulsed” with 10 μg/ml of HBcAg and 2.5 μg/ml of 120–140 for 1 h in the presence or absence of anti-HBc mAbs. Similarly, unprimed spleen cells from either +/+ B6 mice or μMT mice were used as the source of APC in some experiments, and rabbit anti-HBc polyclonal antibodies were used with spleen cell APC. The data are expressed as a percentage of change in T hybridoma IL-2 production because of the presence of anti-HBc antibody as compared with IL-2 production in the absence of antibody. Anti-HBc antibodies inhibited (INH) or enhanced (ENH) HBcAg-specific T hybridoma activation depending on the source of the APC. (C) Inhibition of HBcAg-specific induction of B7.2 mRNA in B cells by anti-mIg and anti-HBc antibodies. Unprimed, splenic B cells derived from B10.S mice were cultured with HBcAg (2.0 μg/ml) or the B cell mitogen LPS (10 μg/ml) without added antibody (0) or in the presence of goat anti-mIg Fab fragments (25 μg/ml) or rabbit anti-HBc polyclonal antibody (1:150) (Dako). After 48 h of culture the B cells were harvested, and the presence of B7.2 and β-actin mRNA was determined by RT-PCR. The RT-PCR was performed as described in Fig. 5. All the experiments depicted in Fig. 3 were performed at least three times, and the results are representative.