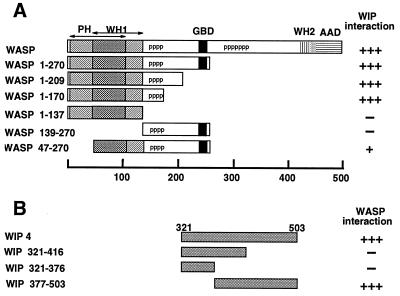
Figure 3.
Mapping of the binding domains of WIP and WASP. (A) Mapping of the WIP binding site of WASP. The domains of WASP are indicated. PH, Pleckstrin homology domain (amino acids 6–105); WH1, WH1 domain (amino acids 47–137); pppppp, proline-rich region; GBD, GTPase binding domain (amino acids 238–257); WH2, WH2 domain (amino acids 423–449); AAD, actin association domain (amino acids 443–502). The numbers under the bar at the bottom of the diagram represent the amino acids of WASP. Truncation mutants of WASP, generated either by PCR or cleavage with appropriate restriction enzymes, were cloned into the pGBT9 vector and examined for WIP binding in the yeast two-hybrid system. Blue color development by β-galactosidase activity was used to score the interaction of WIP with WASP truncations. +++ represents color change in 30 min or less, + represents color change in 3 hr, and − indicates no color change and lack of growth in His− medium. For each mutant at least three independent colonies were tested in the β-galactosidase assay. (B) Mapping of the WASP binding site of WIP. Truncation mutants of WIP4 (amino acids 321–503), generated by cleavage with appropriate restriction enzymes, were cloned into the pGAD424 vector and examined for WASP binding in the yeast two-hybrid system. Interactions were scored as in A.