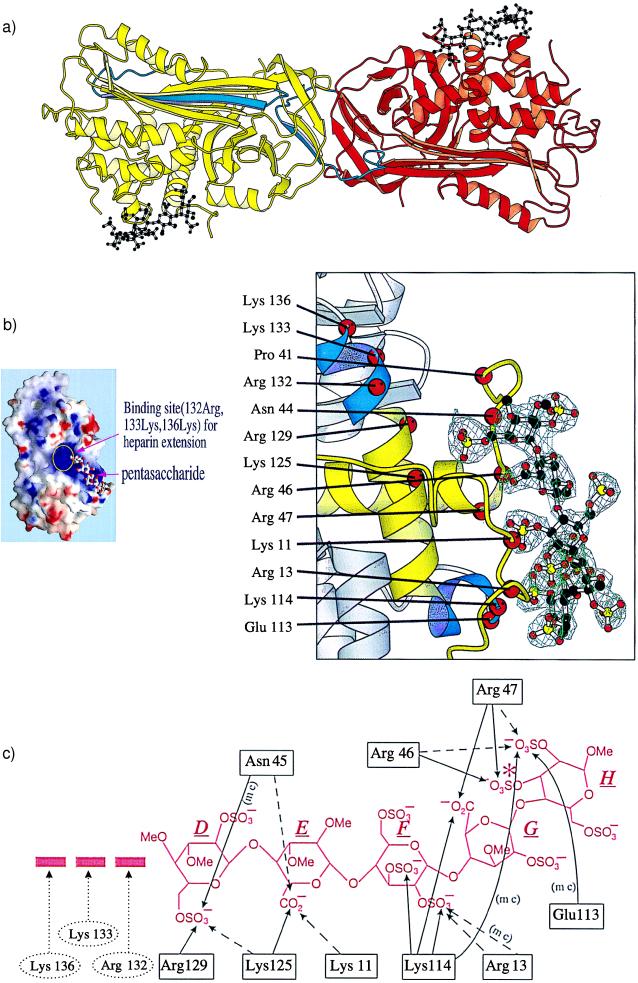
Figure 2.
(a) Dimer of L-antithrombin (yellow) and I-antithrombin (red) each complexed with the pentasaccharide (black). The reactive site loop of each molecule is in blue, the loop being fully inserted in the A β-sheet in L-antithrombin with the reactive loop of the I-antithrombin replacing the vacated strand site s1C in the L-molecule through its P3–P8 residues (amino-terminal to the P1 reactive center). (b) (Left) Electrostatic surface potential map of antithrombin (red, negative potential; blue, positive potential) with the pentasaccharide outline and showing its extension region including 132-Arg, 133-Lys, and 136-Lys. (Right) A σA-weighted difference map, calculated after omitting the pentasaccharide, is displayed at a contour level of 3σ within volume 4 Å around the omitted atoms. Superimposed on the omitmap are the atoms of the pentasaccharide DEFGH (D above) and a ribbon representation of I-antithrombin. The binding site is in yellow and also includes the P-helix, the lower of the two induced helical segments, in blue. (c) Hydrogen bonding to pentasaccharide DEFGH. Likely bonds in full lines, possible bonds in interrupted lines, (mc) indicates main-chain bonding. Arg-132, Lys-133, and Lys-136 are beyond hydrogen bonding distance from the pentasaccharide but could interact with extended oligosaccharides. The extra sulfate present in the high affinity pentasaccharide (16) is asterisked in saccharide H.