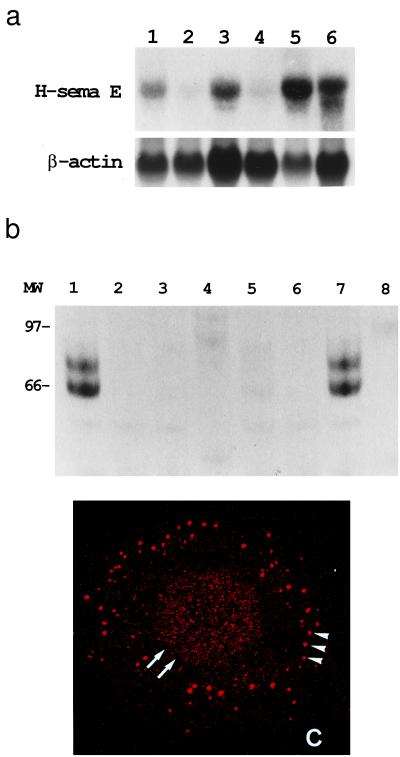
Figure 2.
Overexpression of H-sema E in CDDP-resistant cancer cell lines. (a) Northern blot analysis of H-sema E expression. H-sema E expression was stronger in CDDP-resistant cells (Upper), TYKnuR (lane 1), Lu65/CDDP (lane 3), and MS-1/CDDP (lane 5), than in the CDDP-sensitive parent cells, TYKnu (lane 2), Lu65 (lane 4), and MS-1 (lane 6). The quality and quantity of electrophoresed mRNA was determined by rehybridization of the same blot with β-actin cDNA (Lower). (b) Immunoprecipitation analysis of secreted H-sema E protein. Radio-labeled cell-free conditioned media from Cos-7 cells transfected with H-sema E cDNA (lanes 1 and 2), Cos-7 cells transfected with vector alone (lanes 3 and 4), CDDP-sensitive TYKnu cells (lanes 5 and 6), and CDDP-resistant TYKnuR cells (lanes 7 and 8) were immunoprecipitated with anti-H-sema E antibody (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7) or normal rabbit IgG (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8). (c) Laser scanning confocal immunofluorescence microscopy showing the subcellular localization of H-sema E protein in a CDDP-resistant TYKnuR cell. Dot-like staining of H-sema E in the periphery of the cytoplasm (arrowheads) and diffuse fine granular staining in the entire nucleus (arrows) are evident.