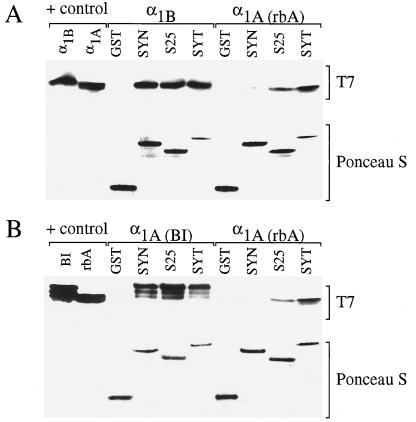
Figure 1.
Binding of α1B, α1A(rbA), and α1A(BI) to SNARE proteins. GST-fusion proteins containing synaptotagmin, syntaxin, SNAP-25, or GST alone (50 pmol) were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose beads. After 60 min, the beads were washed three times with Tris-saline buffer (100 mM Tris⋅HCl/140 mM NaCl/0.1% Triton X-100, pH 8). Purified His-tagged Ca2+ channel fusion proteins from α1B (50 pmol), α1A(rbA) (1.3 nmol), or α1A(BI) (300 pmol) were added to the beads as indicated in the figure. The mixture was then incubated at 4°C for 3 h on a rotating mixer. The Tris-saline buffer containing 15 μM Ca2+ was used for the binding and for the washes. The fusion proteins were then eluted with 20 μl elution buffer (15 mM reduced-glutathione in Tris-saline buffer, pH 8). The eluate was boiled in Tricine sample buffer for 2 min, and the proteins were separated on 10–20% Tricine–SDS/PAGE gradient gels and electrophoretically transferred overnight to nitrocellulose. Separated bands were immunoblotted with T7 monoclonal antibody and visualized with the ECL system (Amersham). Concentrations of GST fusion protein in each condition were visualized by staining with Ponceau S. A positive control indicates the level of staining with the T7 mAb for 2.5 pmol of α1B, α1A(rbA), or α1A(BI) added directly to the gel (control). The appearance of multiple bands in this and subsequent figures (e.g., in α1A(BI) samples) is because of minor proteolytic cleavage products of the fusion proteins that retain binding activity.