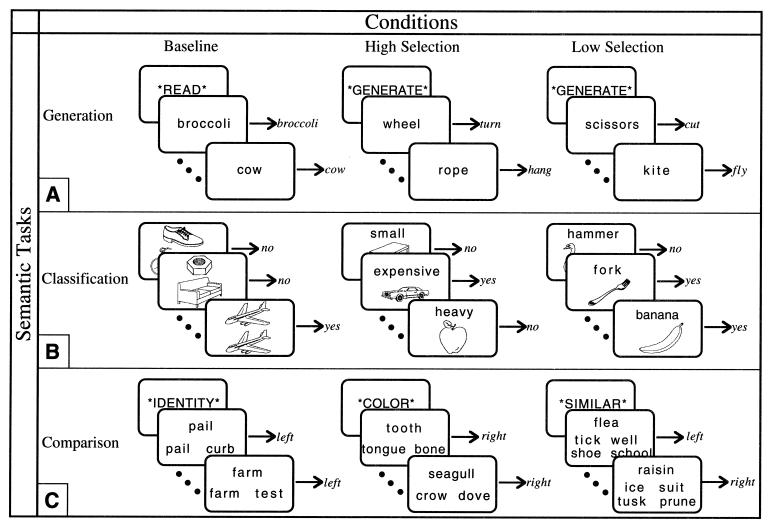
Figure 1.
High Selection, Low Selection, and nonsemantic Baseline conditions of each task were presented in a fixed-order blocked design, one condition per block alternating throughout each scan. For each task, two 12-block scans, separated by 3 min, were run. (A) During the Generation task, subjects either read a word silently [mean (M) response time = 631 ms] or silently generated a related verb. In each condition, subjects were required to indicate completion of the task with a bilateral button press. Each block contained an instruction for 400 ms, followed by 8 words, presented for 2,000 ms with a 400-ms interstimulus interval (ISI). For the Generate conditions, alternate blocks contained either High Selection (M response time = 1211 ms) or Low Selection (M response time = 1,041 ms) items. (B) During the Classification task, subjects classified line drawings of common objects (16). During the High Selection condition, subjects classified 10 pictures according to one of eight different attributes (big, small, light, heavy, manmade, natural, expensive, cheap), randomly presented within the block (M response time = 1188 ms, accuracy = 82%). During the Low Selection condition, subjects classified 10 pictures according to a basic level object name (e.g., spider, hammer) (M response time = 942 ms, accuracy = 99%). During the Baseline condition, subjects classified 10 pictures according to the physical identity of another picture (M response time = 726 ms, accuracy = 99%). On each trial, the stimuli were presented for 1,600 ms followed by a 400-ms ISI. For all items, subjects indicated a yes–no response by pressing one of two buttons. (C) During the Comparison task, subjects made comparisons between a target word and several probe words. In the Baseline condition subjects picked which of two words was the same as the target word (M response time = 664 ms). In the Low Selection condition subjects picked which of either two words (two-choice Low Selection, not pictured; M response time = 1,215 ms) or four words (four-choice Low Selection; M response time = 1,417 ms) was most similar in meaning to the target word. In the High Selection condition subjects picked which of two words was most similar along a specified dimension (color, function, or shape) to the target word (M response time = 1,463 ms); the dimensions were blocked so that in a given block attribute judgments were made about only one dimension but across the experiment there were two blocks of each dimension. Subjects indicated whether the correct probe was on the left or right of the target by pressing a corresponding button. (In the four-choice Low Selection condition, two words were presented on the left and two on the right; although there were four words, the choice was still binary.) Each block began with an instruction cue for 2,000 ms, followed by 9 words, presented for 1,800 ms with a 200 ms ISI.