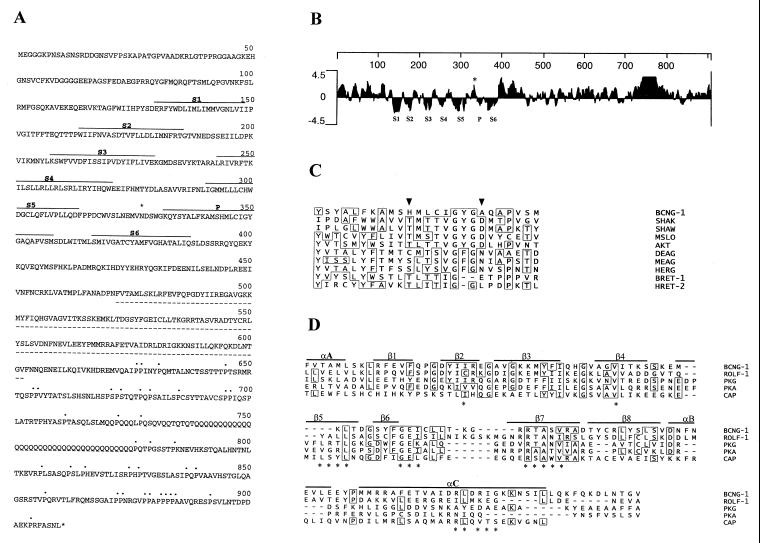
Figure 1.
Primary structure of BCNG-1. (A) Deduced amino acid sequence encoded by the BCNG-1 cDNA. Hydrophobic domains homologous to the six transmembrane domains (S1–S6) and pore (P) of K+ channels are indicated (———). The putative CNBs (- - - - -), C-terminal prolines (⋅⋅⋅), and the consensus N-glycosylation site with presumptive extracellular localization (∗) are also marked. (B) Kyte and Doolittle hydropathy plot of the predicted amino acid sequence of BCNG-1. Hydrophobic regions corresponding to S1 through S6 and the P region lie below the zero line while the N-glycosylation site (∗) is in a hydrophilic region between S5 and P. Numbering (top line) indicates position in the BCNG-1 sequence. Profile generated with a window size of seven residues. (C) Multiple alignment of the putative P region of BCNG-1 with the P regions of Drosophila Shaker (SHAK, refs. 32 and 33), Drosophila Shaw (SHAW, ref. 31), mouse Slo (MSLO, ref. 46), Arabidopsis AKT1 (AKT, ref. 26), Drosophila Eag (DEAG, ref. 34), mouse Eag (MEAG, ref. 26), human Erg (HERG, ref. 26), α-subunit of bovine retinal CNG channel (BRET-1, 36), and β-subunit of human retinal CNG channel (HRET-2, 27). Arrowheads mark residues 344 and 352 (see Results). (D) Alignment of the CNBs of BCNG-1 with the corresponding site in the rat olfactory CNG channel (ROLF-1, ref. 47), bovine cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG, ref. 25), bovine cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA, ref. 25), and catabolite activator protein of Escherichia coli (CAP, ref. 25). Continuous lines mark α-helical (α) and β-strand (β) elements of the secondary structure of catabolite gene activator protein, while asterisks indicate specific amino acids that appear to lie close to the cAMP molecule in the catabolite gene activator protein crystal structure.