Abstract
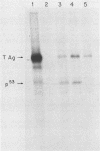
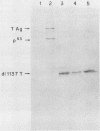
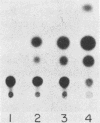
The large tumor antigen (T antigen) of simian virus 40 is necessary and sufficient for the neoplastic transformation of a number of established cell lines. Mutational analysis has revealed that a biochemical activity residing within the amino-terminal 121 amino acids of T antigen is sufficient to induce the transformation of some cell lines, such as C3H10T1/2. The same domain of the molecule also encodes the transactivation function of T antigen and the ability to complex with the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. However, the transformation of other lines, such as REF52, requires an additional activity that is affected by mutations in other portions of the molecule.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asselin C., Bastin M. Sequences from polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T genes capable of immortalizing primary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):958–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.958-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikel I., Montano X., Agha M. E., Brown M., McCormack M., Boltax J., Livingston D. M. SV40 small t antigen enhances the transformation activity of limiting concentrations of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck N., Beales N., Shenk T., Berg P., di Mayorca G. New region of the simian virus 40 genome required for efficient viral transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2473–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butel J. S., Jarvis D. L. The plasma-membrane-associated form of SV40 large tumor antigen: biochemical and biological properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 28;865(2):171–195. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Peden K., Pipas J. M., Nathans D., Tjian R. Biochemical activities of T-antigen proteins encoded by simian virus 40 A gene deletion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):220–228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Murphy D., Lovett M., Rigby P. W. A fragment of the SV40 large T-antigen gene transforms. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):59–61. doi: 10.1038/299059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Shenk T. Fragments of the simian virus 40 transforming gene facilitate transformation of rat embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Rifkin D. B., Topp W. C. Requirement for the large T and small T proteins of SV40 in the maintenance of the transformed state. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):325–331. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbour J. W., Lai S. L., Whang-Peng J., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Kaye F. J. Abnormalities in structure and expression of the human retinoblastoma gene in SCLC. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):353–357. doi: 10.1126/science.2838909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Currie G. A. Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):651–654. doi: 10.1038/312651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., To H., Shew J. Y., Bookstein R., Scully P., Lee W. H. Inactivation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene in human breast cancers. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.3388033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeken M. R., Khoury G., Brady J. Stimulation of the adenovirus E2 promoter by simian virus 40 T antigen or E1A occurs by different mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2020–2026. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeken M., Bikel I., Livingston D. M., Brady J. trans-activation of RNA polymerase II and III promoters by SV40 small t antigen. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1171–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Nicolas J. C., Topp W. C., Girard M., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Transformation by adenovirus early region 2A temperature-sensitive mutants and their revertants. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Setlow V. P., Edwards C. A., Vembu D. The roles of the simian virus 40 tumor antigens in transformation of Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Eliyahu D., Oren M. Overproduction of protein p53 contributes to simian virus 40-mediated transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3531–3536. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Fischer-Fantuzzi L., Vesco C., Pipas J. M., Oren M. Activated Ha-ras can cooperate with defective simian virus 40 in the transformation of nonestablished rat embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2648–2654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2648-2654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole S. E., Gannon J. V., Ford M. J., Lane D. P. Structure and function of SV40 large-T antigen. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):455–469. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Nathans D. Local mutagenesis within deletion loops of DNA heteroduplexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7214–7217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Srinivasan A., Farber J. M., Pipas J. M. Mutants with changes within or near a hydrophobic region of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen are defective for binding cellular protein p53. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit C. A., Gardes M., Feunteun J. Immortalization of rodent embryo fibroblasts by SV40 is maintained by the A gene. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):74–82. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B., Rundell K. Failure of simian virus 40 small t antigen to disorganize actin cables in nonpermissive cell lines. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):768–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.768-775.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif R., Martin R. G. Simian virus 40 small t antigen is not required for the maintenance of transformation but may act as a promoter (cocarcinogen) during establishment of transformation in resting rat cells. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):979–988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.979-988.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Topp W. C., Hanich R., Sambrook J. F. Mutants of SV40 with an altered small t protein are reduced in their ability to transform cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Gurney E. G., Danna K. J. Stabilization of the 53,000-dalton nonviral tumor antigen is not required for transformation by simian virus 40. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):290–296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. A new SV40 mutant that encodes a small fragment of T antigen transforms established rat and mouse cells. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90279-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. Less than 40% of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen-coding sequence is required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1661–1663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. Simian virus 40 deletion mutants that transform with reduced efficiency. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):484–489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. The simian virus 40 sequences between 0.169 and 0.423 map units are not essential to immortalize early-passage rat embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1191–1194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack L. C., Cartwright C. A., Wright J. H., Eckhart W., Peden K. W., Srinivasan A., Pipas J. M. Properties of a simian virus 40 mutant T antigen substituted in the hydrophobic region: defective ATPase and oligomerization activities and altered phosphorylation accompany an inability to complex with cellular p53. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3362–3367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3362-3367.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Pipas J. M., Kierstead T., Cole C. Requirements for immortalization of primary mouse embryo fibroblasts probed with mutants bearing deletions in the 3' end of SV40 gene A. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):76–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ronde A., Sol C. J., van Strien A., ter Schegget J., van der Noordaa J. The SV40 small t antigen is essential for the morphological transformation of human fibroblasts. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90534-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]