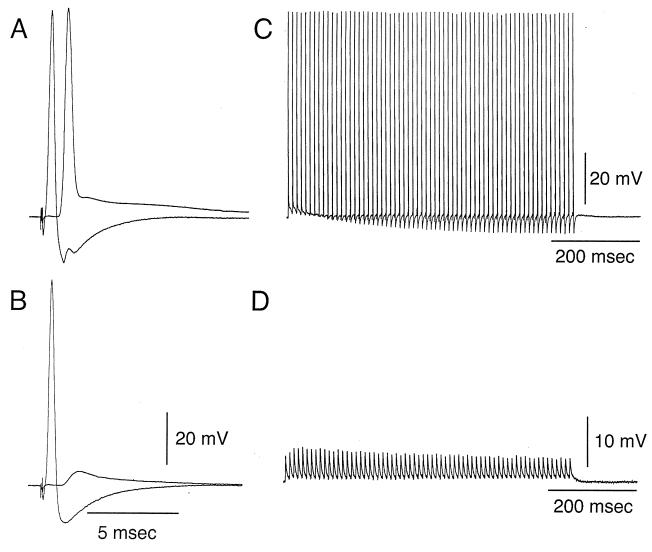
Figure 2.
Transmitter release block as determined by tetanic presynaptic stimulation. (A and B) Presynaptic and postsynaptic response to electrical stimulation of the presynaptic axon. (A) Control. (B) Reduction of postsynaptic response 35 min after presynaptic injection. (C and D) Postsynaptic response to tetanic presynaptic stimulation at 100 Hz. (C) Repetitive postsynaptic response prior to microinjection. (D) Reduction of tetanic postsynaptic response, shown at higher gain (see voltage calibration) 35 min after BoNT/C1-LC microinjection. Note that the amplitude for the postsynaptic potential is maintained close to constant throughout the duration of the tetanus.