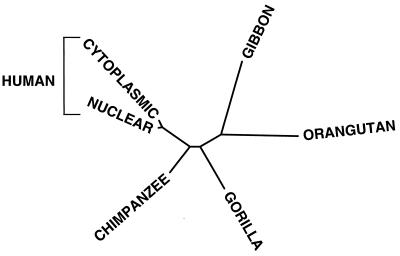
Figure 3.
Unrooted NJ tree relating the human nuclear CO1 and CO2 sequences to the homologous sequences from the human, chimpanzee, gorilla, gibbon, and orangutan mtDNAs. This tree is based on genetic distances calculated using the maximum likelihood model (DNAML) (28). Boostrap analysis from 100 independent trees generated the diagrammed result in 100% of the comparisons between the human nuclear and cytoplasmic sequences and between the gibbon and orangutan sequences, in 99% of the comparisons between the two human sequences and the chimpanzee sequence, and in 82% of the comparisons between the chimpanzee and gorilla sequences and between the gorilla and the collective gibbon and orangutan sequences. Phylogenies with identical branching orders were obtained by using genetic distances calculated by the parsimony, Jukes-Cantor, and Kimura two-parameter methods.