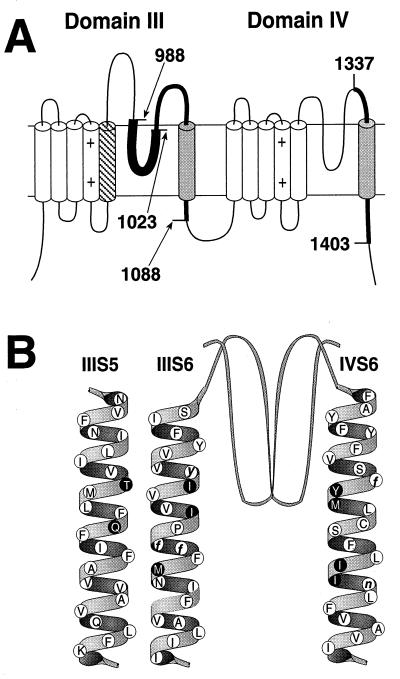
Figure 1.
Localization of the DHP binding site in l-type channels. (A) Studies utilizing DHP photoaffinity labels and site-directed antibodies (28, 29) identified transmembrane segments IIIS6 and IVS6 of l-type Ca2+ channels as components of the DHP binding site. Boundaries of the labeled peptides (shaded cylinders and thick lines) are shown as amino acid sequence numbers from α1S (6). Subsequent studies utilizing chimeric Ca2+ channels further demonstrated the role of IIIS6 and IVS6 as well as transmembrane domain IIIS5 in DHP moduation of l-type channels (32–34). (B) Structure of α1A/DHPS. Studies of single amino acid substitutions in l-type channels revealed nine l-type-specific (black circles with white letters) and five conserved (white circles with black lower case letters) amino acid residues to be critical for DHP binding and block of l-type channels (34–38). The nine l-type-specific amino acid residues critical for DHP action were inserted into the DHP-insensitive α1A subunit amino acid sequence (14) (white circles with black letters) to a construct a mutant α1A subunit that is modulated by DHPs (α1A/DHPS).