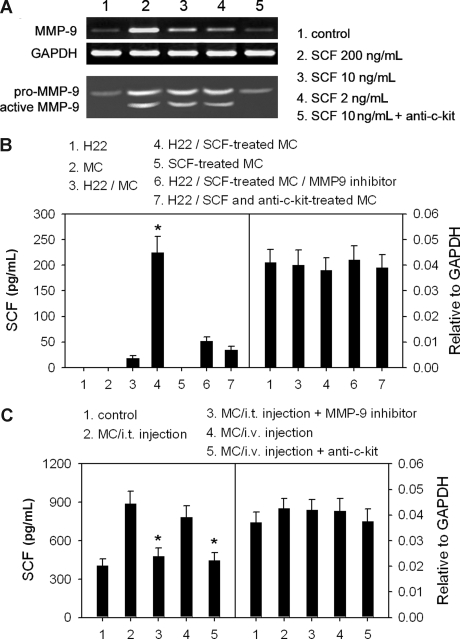
Figure 4.
SCF-stimulated mast cells augment the release of SCF from tumor cells. (A) SCF stimulates the production of active MMP-9 by mast cells (MCs). BMMCs were cultured for 24 hours in the presence of different concentrations of SCF and anti–c-Kit (10 μg/mL). The production of MMP-9 was detected by RT-PCR and gelatin zymography. (B) MC-derived MMP-9 increased the release of SCF from H22 tumor cells. BMMCs were treated with 5 ng/mL of SCF for 4 hours in the absence or presence of 10 μg/mL anti–c-Kit antibody. H22 cells and SCF-treated BMMCs were cultured alone or in 2 chambers separated by semipermeable membrane. SCF in the supernatants was detected by ELISA (left). SCF mRNA was detected by real-time RT-PCR (right). *P < .05, compared with the H22/MC group. (C) Assay of SCF in tumor tissues. Tumor-bearing mice received the intraperitoneal injection of MMP-9 inhibitor and the intratumor (i.t.) injection of MCs, or received the intravenous (i.v.) injection of MCs with anti–c-Kit antibody. The tumor tissues were excised 48 hours after MC injection and cultured in vitro. SCF in the supernatants was detected by ELISA (left). The mRNA level of SCF in tumor tissues was detected by real-time RT-PCR (right). *P < .05, compared with the MC injection groups. Error bars represent SD.