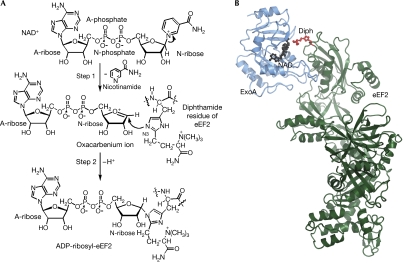
Figure 1.
Reaction mechanism and structure of ExoA. (A) Schematic representation of the reaction catalysed by ExoA. ExoA catalyses the transfer of A-ribose from NAD+ to N3 of the diphthamide imidazole, impairing eEF2 function and causing inhibition of protein synthesis. (B) Ribbon representation of the eEF2–ExoAc–NAD+ complex. The ExoAc (blue) is bound to the diphthamide-containing domain of eEF2 (green) with the diphthamide (Diph; red ball and stick) pointing towards the NAD+ (black ball and stick). A-ribose, ADP ribose; A-phosphate, adenine phosphate; eEF2, elongation factor 2; ExoA, exotoxin A; N-ribose, nicotinamide ribose.