Figure 1. Soybean Itpks: Amino-acid sequences and phylogenetic relationships.

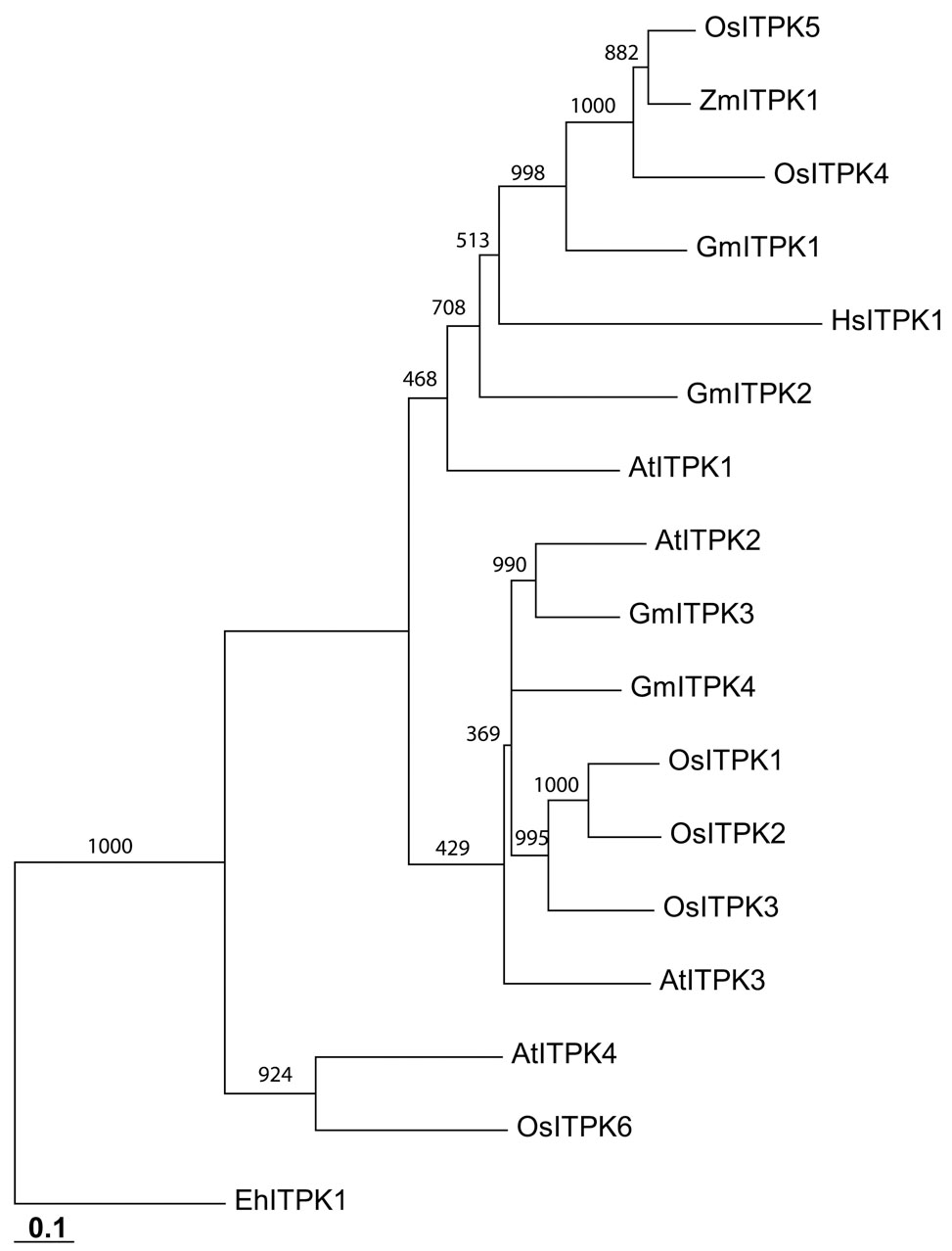
Panel A: Alignment (using ClustalW) of Itpks from the following species (Genbank accession numbers in parentheses): Entamoeba histolytica (Eh; AF118848), Homo sapiens (Hs; NP_055031), Soybean (Gm; type 1, EU033958, type 2, EU033959, type 3, EU033960, type 4, EU033961), Arabidopsis thaliana (At; type 1, Q9SBA5) and Zea mays (Zm; type 1, Q84Y01). The recent publication of the Arabidopsis Itpk gene family (14) led us to renumber the previously designated soybean GmItpk4 sequence (16) as GmItpk2. A small number of C-terminal residues (which show no sequence similarity) are omitted for clarity. Highlighted residues are conserved in at least four of the aligned proteins. Asterisks denote residues in HsITPK which, when mutated, decrease catalytic activity at least 20% (24;25). Panel B shows a phylogram generated with Treeview (26) from a 1000 iteration bootstrap analysis using the sequences described in Panel A, plus additional sequences from Arabidopsis (14) and rice (8). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
