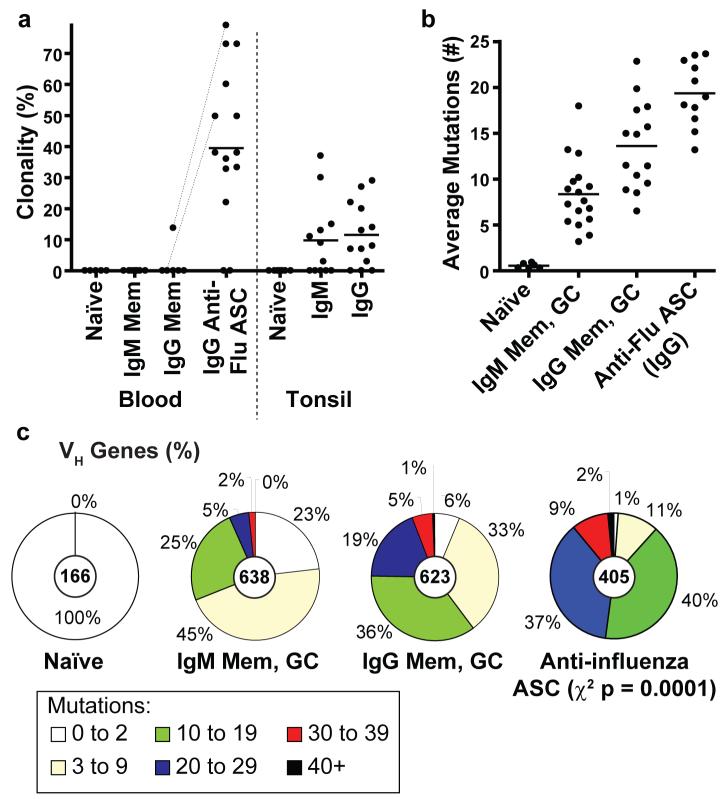
Figure 2. The ASC response after influenza vaccination is pauci-clonal and highly diversified by somatic hypermutation.
a, Comparison of the mean proportion (line) of all clonal variable region sequences from day 7 ASCs of 14 donors (points), including: the bulk RNA of 104 to 105 ASCs from 10 donors and verification by single cell RT-PCR for 4 donors (average 37 sequences per donor). The ASCs were the most clonally-related population (t-test p ≤ 0.0003). Dotted lines indicate donors from which memory and ASCs were analyzed simultaneously. Other B cell populations were from historical data analyzed in a similar fashion from our laboratory15-17 (see Methods, Supplemental data at Nature online) b, Each point is the average frequency of somatic mutations per sequence from each donor (n values within Methods). On average the anti-influenza ASCs had accumulated more mutations than either the IgG (t-test p =0.003) or IgM (p = <0.0001) memory and GC populations. c, Indicated is the proportion of all variable genes from each B cell population with the number of somatic mutations denoted in the legend (n-values are at the center of each pie chart).