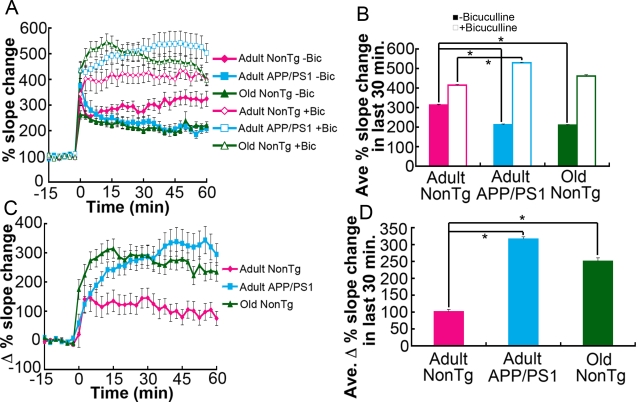
Figure 3. Enhanced GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition reduces LTP in adult APP/PS1 and old nonTg mice.
(A) LTP in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus was recorded in the absence and presence of bicuculline to estimate the extent of GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition. In aCSF-bathed slices, tetanus-induced LTP expression in adult APP/PS1 and old nonTg mice was smaller than that in slices from adult nonTg mice. In contrast, in the presence of bicuculline, LTP in slices from adult APP/PS1 and old nonTg mice was larger than that in slices from adult nonTg mice. (B) Data collected from the last 30 min in (A) were averaged. The means of the three groups in each condition with or without bicuculline showed significant differences in the Friedman test (p<0.0001). However, the Dunn's multiple comparison test (*p<0.001) showed a significant difference between adult nonTg and adult APP/PS1 but not between adult nonTg and old nonTg in the presence of bicuculline. (C) The averaged data in the condition without bicuculline was subtracted from the data in the condition with bicuculline, showing the higher extent of inhibition mediated by GABAA receptors in adult APP/PS1 and old nonTg mice. (D) The values from the last 30 min in (C) were averaged; *p<0.0001; two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. The numbers of slices and mice used in each condition were as follows: bicuculline-treated slices–17 slices from 9 adult nonTg mice, 24 slices from 9 adult APP/PS1 mice, and 20 slices from 5 old nonTg mice; untreated slices–13 slices from 9 adult nonTg mice, 16 slices from 9 adult APP/PS1 mice, and 22 slices from 5 old nonTg mice. The ages of mice were 9–11 months (9.3±0.7 months) for adult nonTg; 9–11 months (9.5±0.9 months) for adult APP/PS1; and 20–24 months (22.7±2.0 months) for old nonTg mice. The nonTg mice used for LTP measurements were nonTg littermates and controls from a variety of transgenic lines, all having in common the C57BL/6J background strain.