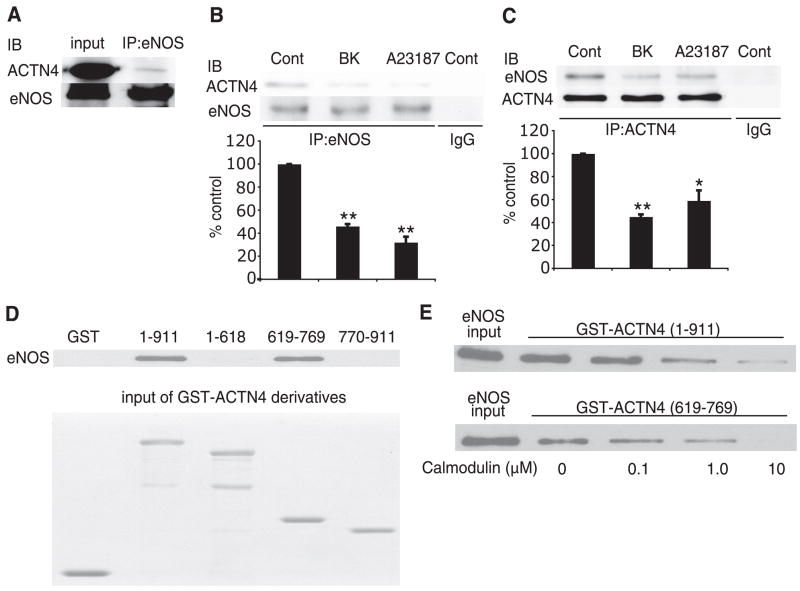
Figure 3.
Interaction of α-actinin-4 with eNOS. A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of eNOS from human endothelial cell lysates with anti-eNOS antibody followed by immunoblotting with α-actinin-4 antibody. Experiments were performed 3 times with similar results. B) Lysates from untreated endothelial cells (Cont) or endothelial cells stimulated with bradykinin (BK, 1 μM) or the calcium ionophore A23187 (10 μM) were immunoprecipiated (IP) with eNOS antibody followed by immunoblotting with α-actinin-4 antibody. Experiments were performed 3 times with similar results. C) Lysates from untreated endothelial cells (Cont) or endothelial cells stimulated with bradykinin (BK, 1 μM) or the calcium ionophore A23187 (10 μM) were immunoprecipiated (IP) with α-actinin-4 antibody followed by immunoblotting with eNOS antibody. Densitometry analysis in bar graph. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared with control. Experiments were performed 3 times with similar results. D) GST-ACTN4 pull-down assay using various deletional constructs of ACTN4 and recombinant bovine eNOS protein. Experiments were performed 3 times with similar results. E) Dose-dependent effects of calmodulin on eNOS interaction with GST-ACTN4 constructs. Note that calmodulin inhibited the interaction of eNOS with either GST-ACTN4 (1–911 aa) or GST-ACTN4 (619–769 aa). Experiments were performed 3 times with similar results.