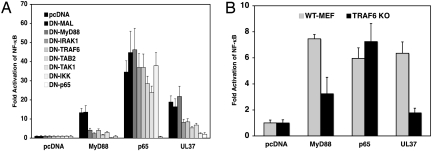
Fig. 2.
Identification of cellular signaling molecules needed for NF-κB activation by UL37. (A) Use of dominant-negative mutant genes. Plasmid DNAs (20 ng) encoding dominant-negative mutant forms of MAL, MyD88, IRAK1, TRAF6, TAK1, TAB2, IKK, or p65 were cotransfected with 20 ng of UL37, MyD88, or p65 plasmid DNAs, together with 20 ng of NF-κB reporter plasmid DNA and 5 ng of control plasmid DNA into HEK293 cells. At 24 h after transfection, the NF-κB fold activation was determined as in Fig. 1A. (B) Use of a TRAF6 knockout MEF cell line. WT MEF or TRAF6 knockout MEF cells were transfected with 100 ng of MyD88, p65, UL37, or empty vector plasmid, together with 100 ng of NF-κB reporter plasmid and 20 ng of control plasmid. At 24 h after transfection the NF-κB fold activation was determined as in Fig. 1A.