Fig. 1.
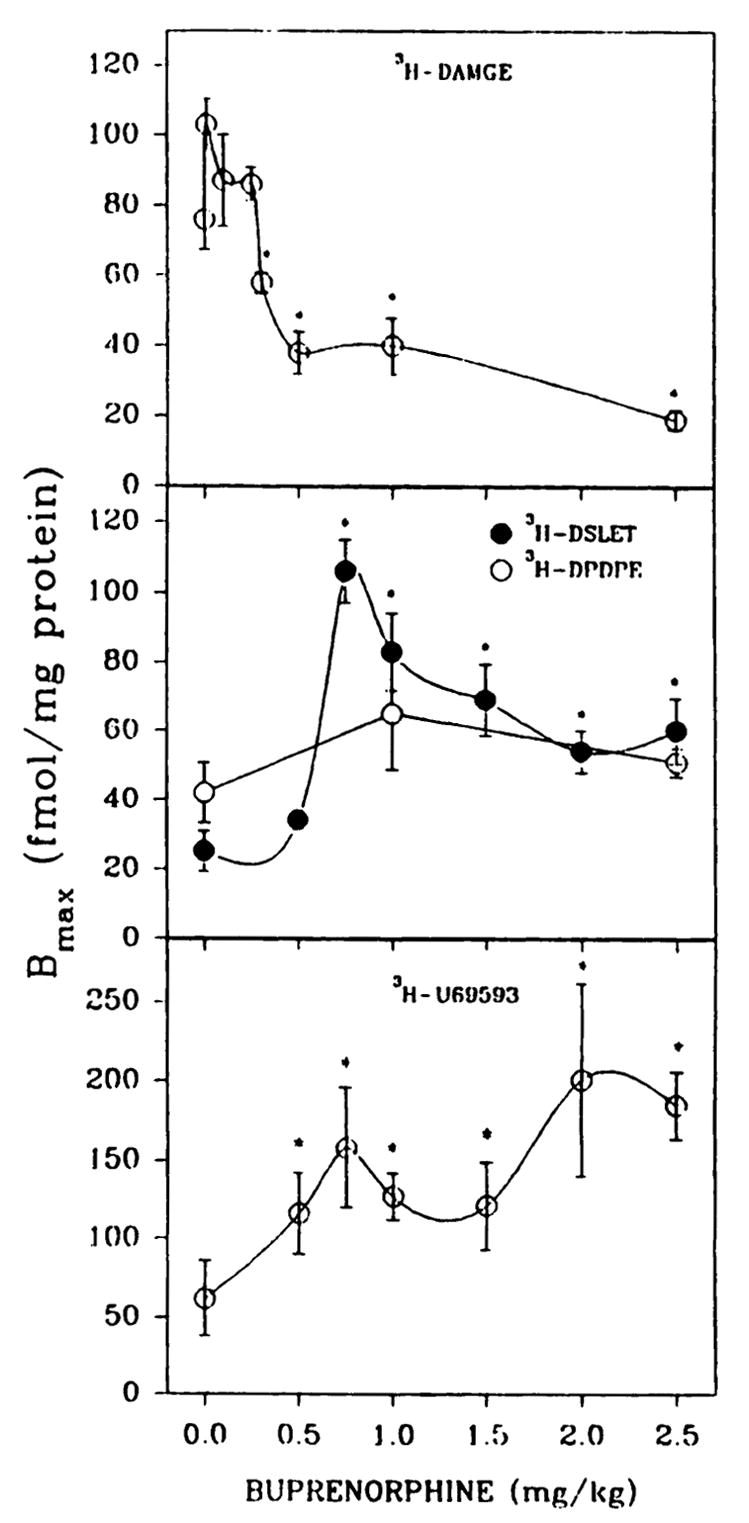
Opioid binding to brain membrane preparations from P7 rats treated in vivo with various concentrations of buprenorphine. Pups were given subcutaneous injections of saline or buprenorphine daily for 6 days and were sacrificed 20 hr after the last administration. Brain membranes were washed five times with 25–30 ml of 50 mM Tris·HCl, pH 7.4, before binding assays. Opioid binding was measured with 1 nM [3H]DAMGE, [3H]DSLET, or [3H]U69593 or 2 nM [3H]DPDPE in 12-point homologous competition assays. Bmax, and Kd values were estimated using the LIGAND program. The affinity of [3H]DAMGE (μ) is shown in Fig. 3. In the order of increasing buprenorphine concentrations from 0 to 2.5 mg/kg, Kd values were 3.3 ± 0.6, 3.3 ± 0.2, 7.6 ± 1.2, 6.2 ± 1.1, 2.8 ± 0.2, 6.0 ± 0.9, and 5.1 ± 0.7 nM ([3H]DSLET); 3.8 ± 0.6, 5.3 ± 1.3, and 3.4 ± 0.2 nM ([3H]DPDPE); and 3.1 ± 0.7, 5.1 ± 0.9, 4.2 ± 0.8, 6.4 ± 0.9, 4.9 ± 1.2, 5.8 ± 1.4, and 4.9 ± 0.3 nM ([3H]U69593). *, Significantly different from saline treated, p < 0.05. Results are from four to seven separate experiments.
