Abstract
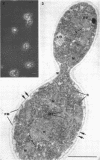
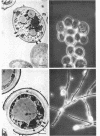
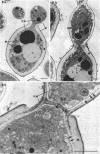
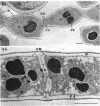
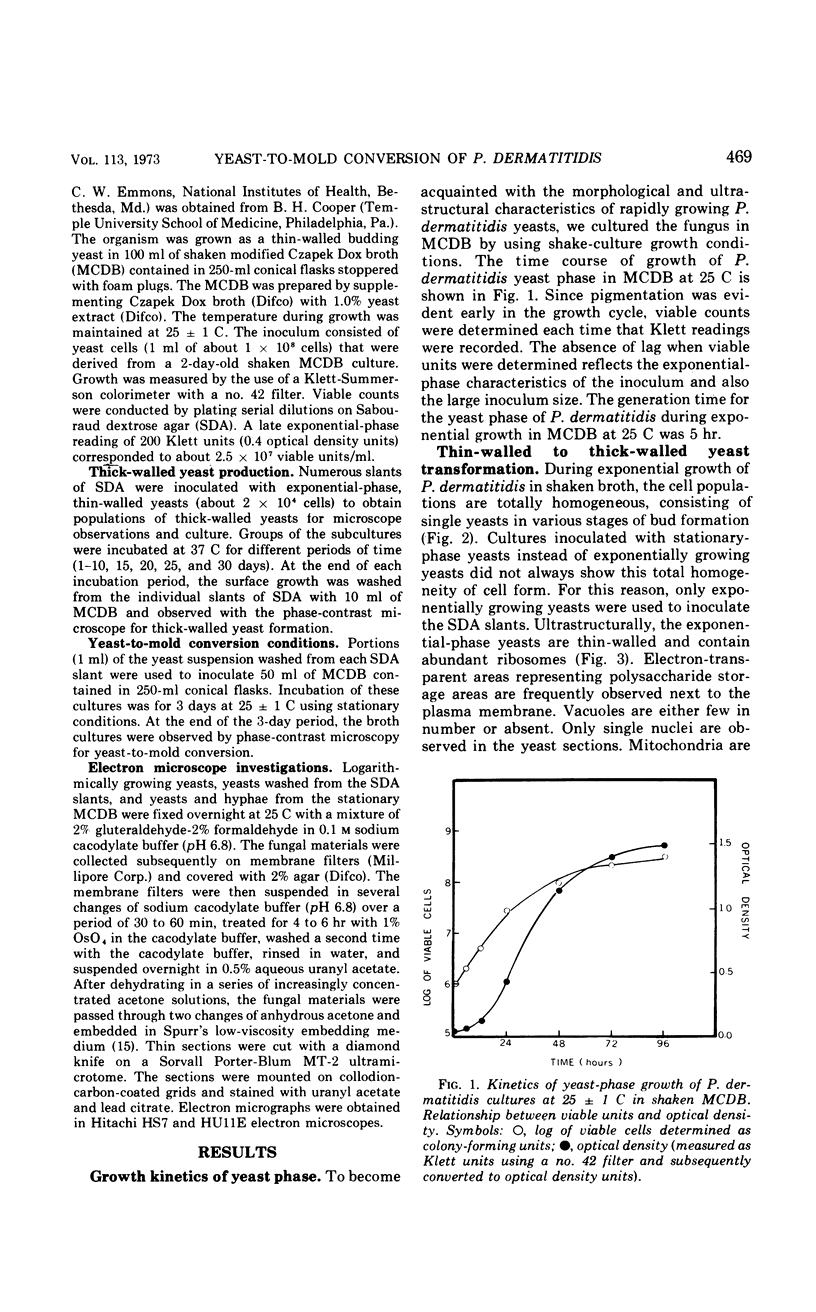
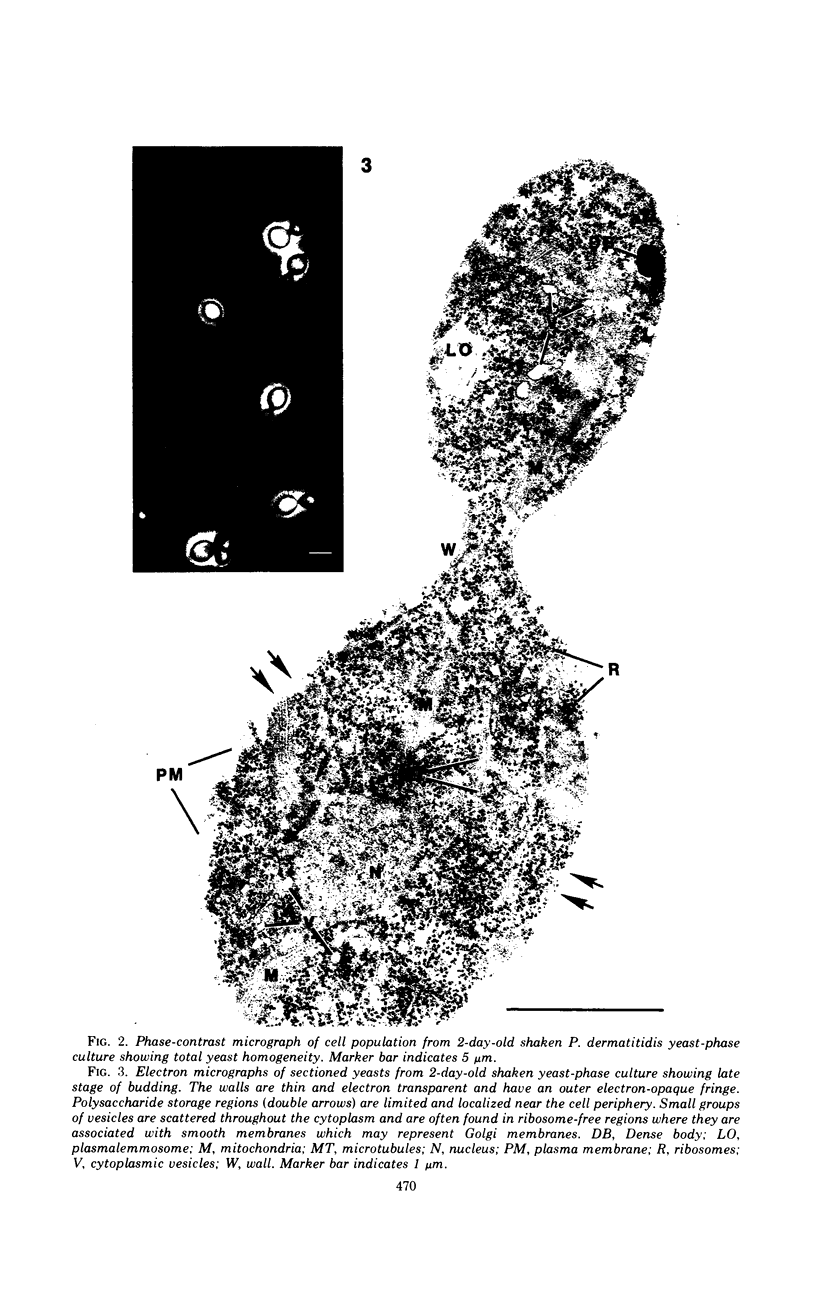
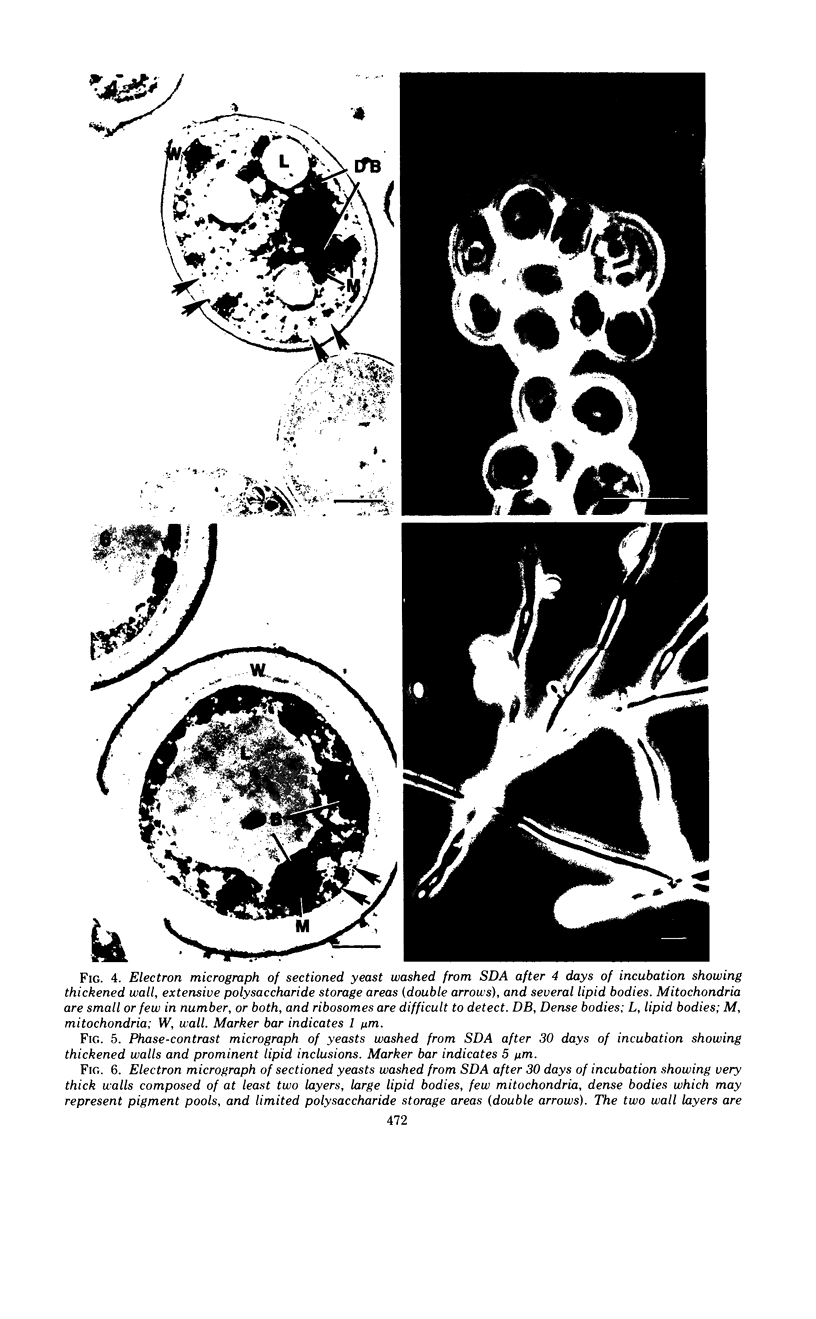
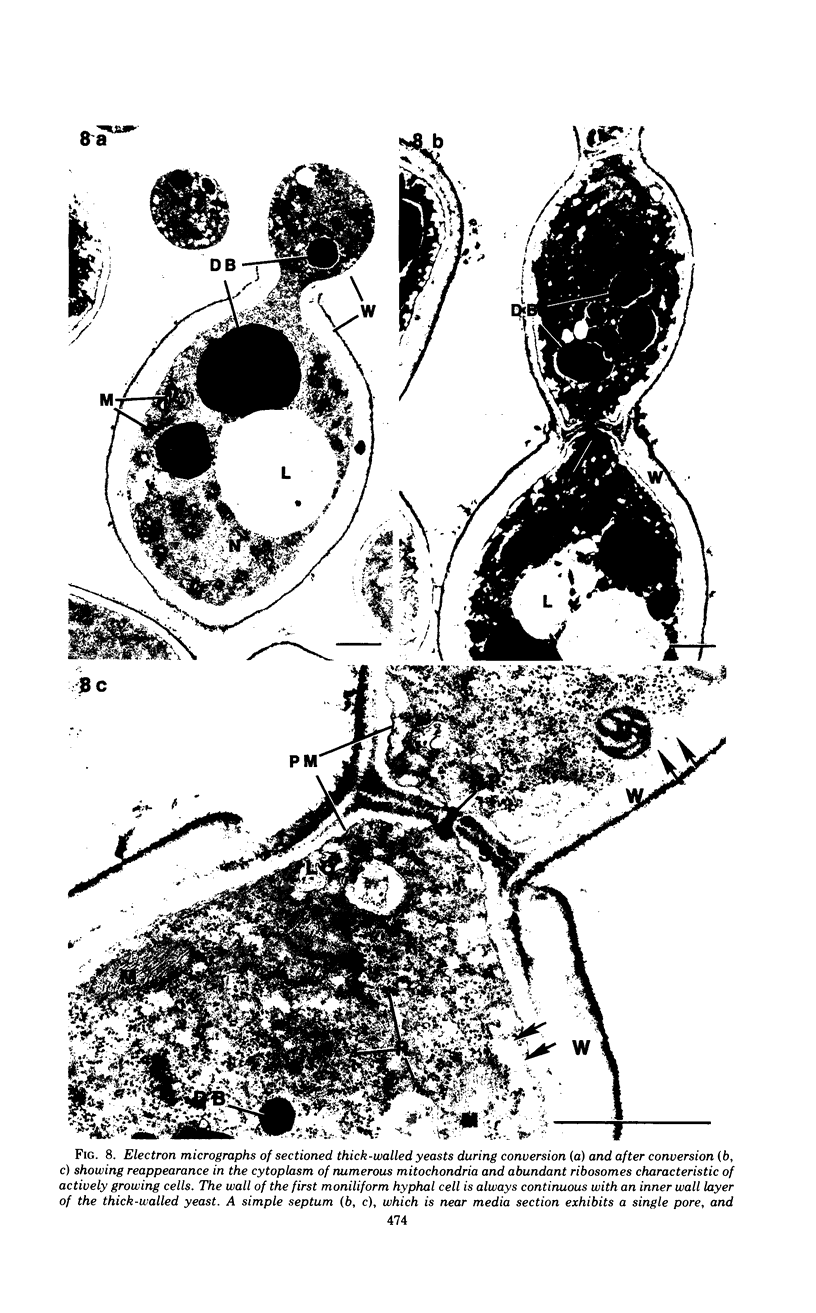
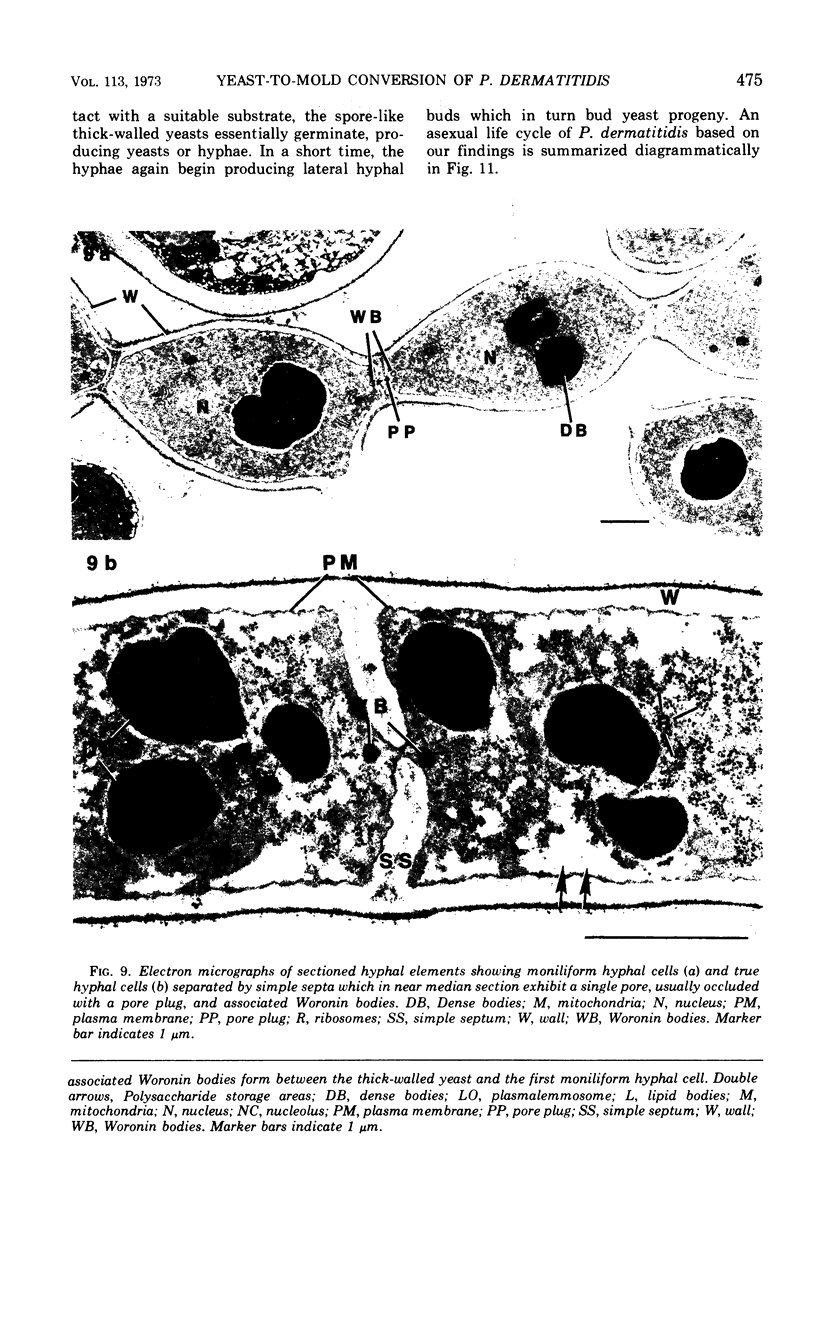
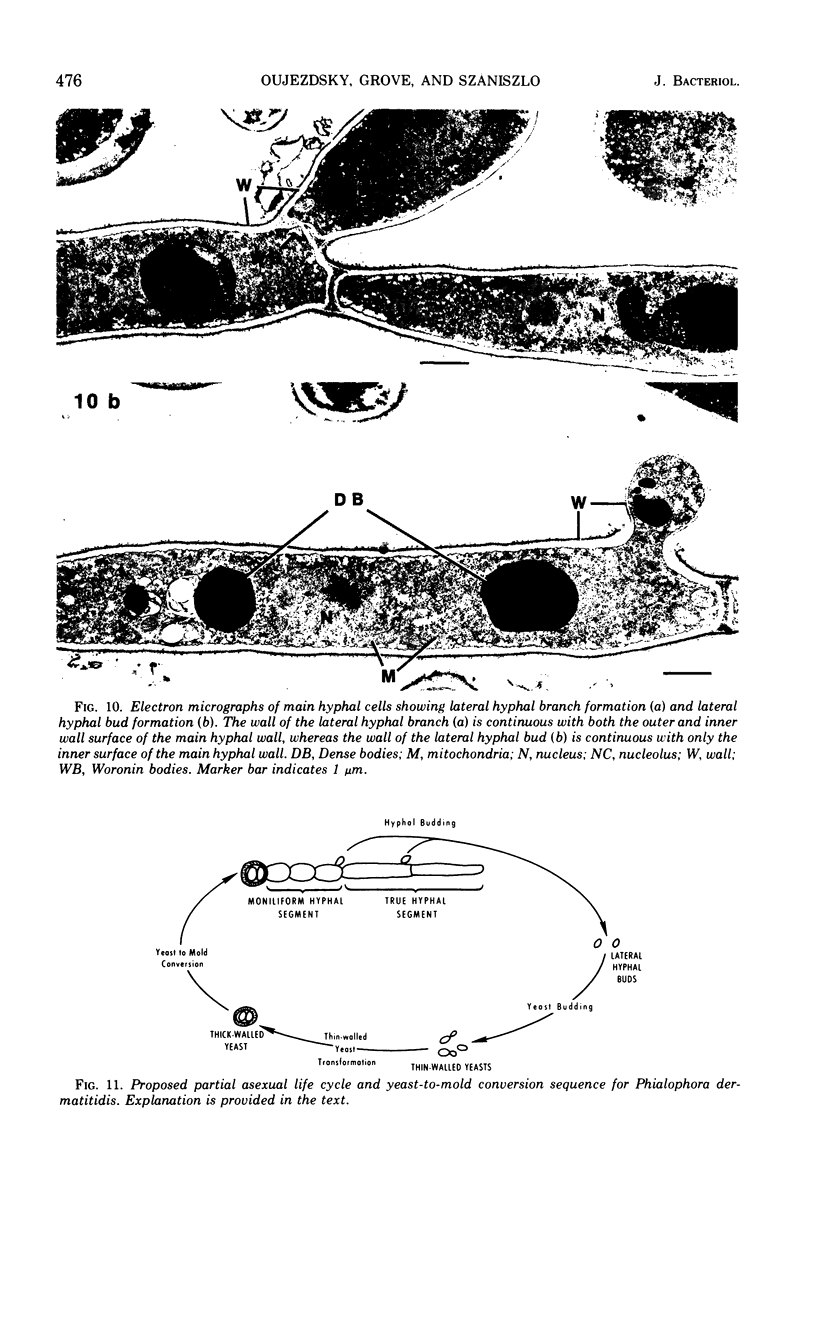
The details of the morphological and structural events occurring during yeast-to-mold conversion of the human pathogenic fungus Phialophora dermatitidis as seen by phase-contrast microscopy and electron microscopy are described and illustrated. Budding yeasts growing exponentially were observed to have thin walls and a cytoplasm exhibiting the characteristics of rapidly growing cells including numerous mitochondria, abundant ribosomes, few vacuoles, and little accumulation of storage material. In contrast, thick-walled yeasts were characterized by less apparent or significantly fewer mitochondria and ribosomes and the presence of considerable amounts of storage materials. Microscope observations of yeast-to-mold conversion revealed that only thick-walled yeasts having prominent lipid bodies in their cytoplasm converted to hyphal forms. Typically, the thick-walled yeast formed two to a number of moniliform hyphal cells which in turn often produced true hyphae. The results indicated that yeasts of P. dermatitidis must acquire spore-like characteristics by becoming thick-walled and by accumulating considerable endogenous substrate reserves before they convert and produce hyphae.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell C. K. Fine structure of vegetative hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):373–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonell L. M. Ultrastructure of dimorphic transformation in paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1076–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1076-1082.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison R. G., Lane J. W., Field M. F. Ultrastructural changes during the yeastlike to mycelial-phase conversion of Blastomyces dermatitidis and Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):628–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.628-635.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison R. G., Lane J. W., Johnson D. R. Electron microscopy of the transitional conversion cell of Histoplasma capsulatum. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1971 May 3;44(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF02051880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD D. H. The morphogenesis of the parasitic forms of dimorphic fungi. A review. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1962 Oct 10;18:127–139. doi: 10.1007/BF02055153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jotisankasa V., Nielsen H. S., Jr, Conant N. F. Phialophora dermatitidis; its morphology and biology. Sabouraudia. 1970 Aug;8(2):98–107. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane J. W., Garrison R. G. Electron microscopy of the yeast to mycelial phase conversion of Sporotrichum schenckii. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):747–749. doi: 10.1139/m70-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatsu L. Y., Jacks T. J., Hensarling T. P. Isolation of spherosomes (oleosomes) from onion, cabbage, and cottonseed tissues. Plant Physiol. 1971 Dec;48(6):675–682. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharuk R. Y. Ultrastructural changes in tissues of larval Elateridae (Coleoptera) infected with the fungus Metarrhizium anisopliae. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):281–289. doi: 10.1139/m71-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalokar M. Intracellular centrifugal separation of organelles in Phycomyces. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):494–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]