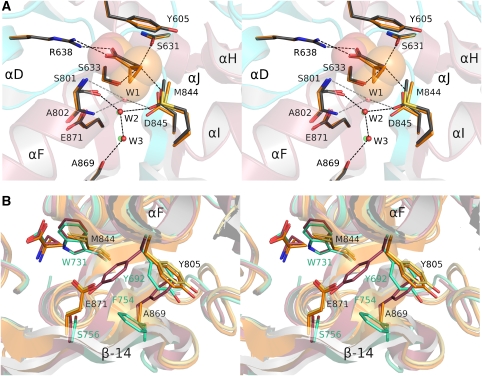
Figure 5.
Mechanism of binding of ACPC. (A) NR3A complexes with ACPC and glycine superimposed by least squares using domain 1 Cα coordinates; carbon atoms for ligands, and side chains for the ACPC and glycine complexes are shaded orange and grey, respectively; the ACPC ligand is shown as transparent CPK spheres; water molecules for the ACPC and glycine complexes are drawn in green and red, respectively. (B) Superpositions of the NR3A glycine (yellow) and ACPC (orange) and NR1 glycine (green) and ACPC (magenta) complexes reveal that, in contrast to the strikingly different conformations observed in the NR1 complexes, there is no ligand-dependent conformational switch in helix F and β-strand 14 for the NR3A complexes; side-chain labels are coloured black for NR3A and green for NR1.