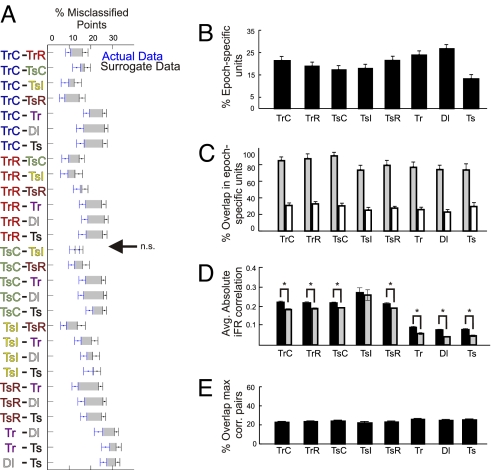
Fig. 2.
Summary statistics revealing distinct network states in terms of both firing rate properties and correlations for each task epoch. (A) Separability between any two epochs in MUA space was quantified as the percentage of incorrectly classified points in the original data set (blue points and error bars) relative to those in the surrogates (black points and error bars) averaged across all datasets. Error bars = SEM. The gray shadings between the error bars surrounding the means of the original and surrogate data highlight the degree of difference between them. All pairs of task epochs were statistically separable except for the comparison TsC − TsI as indicated by the arrow. (B) The percentage of cells that have a significant iFR selectivity index for each task epoch. (C) For each task epoch, the percentage of the epoch-selective cells shown in B that exhibited a significant modulation of their firing rate in at least one other epoch (gray bars), and the percentage of selective cells shared on average with any one of the other epochs (white bars). The light-gray bars provide an indication of how many cells are involved in multiple task epochs, whereas conversely the white bars indicate how well the subpopulation of cells with significant selectivity can dissociate between any two task epochs. (D) For each task epoch, averaged (across all cell pairs and datasets) absolute iFR correlations ± SEM for the original data (black bars) and for surrogates composed of shuffled iFR bins (gray bars). For all task epochs, the differences between correlations among the original iFR time series and those within the shuffled surrogates were significant as denoted by an asterisk, except for the incorrect choice epoch. (E) Relative proportion of the 20% highest-correlated pairs a given task epoch shares on average with any other task epoch. The relatively low values indicate that the cell pairs exhibiting the strongest functional couplings change from one task epoch to the next.