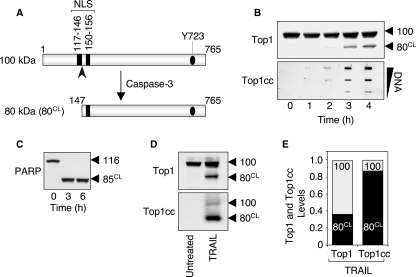
FIGURE 4.
The caspase-3-cleaved Top1 catalytic polypeptide preferentially forms the apoptotic Top1cc induced by TRAIL. A, schematic representation of caspase-3-induced cleavage of Top1. Caspase-3 cleaves the 100-kDa native Top1 polypeptide after aspartate residue 146 (indicated by the arrowhead), and generates an 80-kDa C-terminal fragment (80CL) that still possesses one of the two nuclear localization signals (NLS) and the active site tyrosine (Tyr723, Y723) of the enzyme. B, time course of apoptotic Top1 cleavage and Top1cc in response to TRAIL. HCT116 cells were treated with 0.1 μg/ml TRAIL for the indicated times. Top panel, whole cell extracts were examined for caspase-mediated cleavage of Top1 by Western blotting. Molecular mass of Top1 polypeptide and its cleaved product (CL) are indicated at right. Bottom panel, detection of Top1cc. The DNA-containing fractions were pooled and probed at three concentrations (10, 3, and 1 μg) with an antibody against Top1. C, PARP is completely processed in response to TRAIL. HCT116 cells were treated with 0.1 μg/ml TRAIL for the indicated times. Whole cell extracts were examined for caspase-mediated cleavage of PARP by Western blotting. Molecular mass of PARP polypeptide and its cleaved product (CL) are indicated at right. D, the Top1 cleavage fragment is preferentially involved in the apoptotic Top1cc. HCT116 cells were treated with 0.1 μg/ml TRAIL for 18 h. Western blotting analyses of Top1 in whole cell extracts (top panel) and in the DNA-containing fractions isolated from CsCl gradient centrifugation (bottom panel) (see “Experimental Procedures”). E, quantification of the data shown in panel D. The 100-kDa native Top1 (100) is shown in gray, and the 80-kDa cleaved Top1 (80CL) is shown in black. Similar results were obtained following a 4-h TRAIL exposure (data not shown).