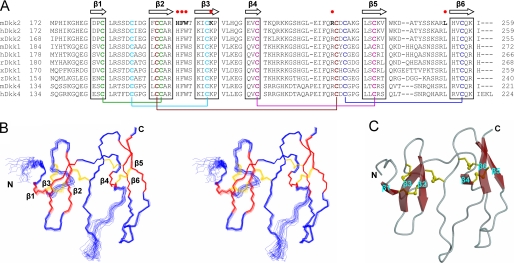
FIGURE 2.
Solution structure of Dkk2C. A, amino acid sequence alignment of C-terminal cysteine-rich domains of Dkks in mouse (m), human (h), Xenopus (x), rabbit (r), and zebrafish (z).β strand elements identified in the three-dimensional structure of Dkk2C are indicated at the top. Ten conserved cysteines are in bold type, and pairs of cysteines forming disulfide bridges are colored identically and linked by lines. Amino acids that contact the third β-propeller domain of LRP5 in the docked model are in bold and indicated by the red dots. B, stereo view of the peptide backbone (N, C-α, C′) determined by superimposition of 20 conformers of Dkk2C with the lowest target function values. The figure was generated by using MOLMOL (39). β strands are red; disulfide bridges are yellow. C, ribbon diagram of Dkk2C with the lowest target function values, generated by using MOLSCRIPT (40).