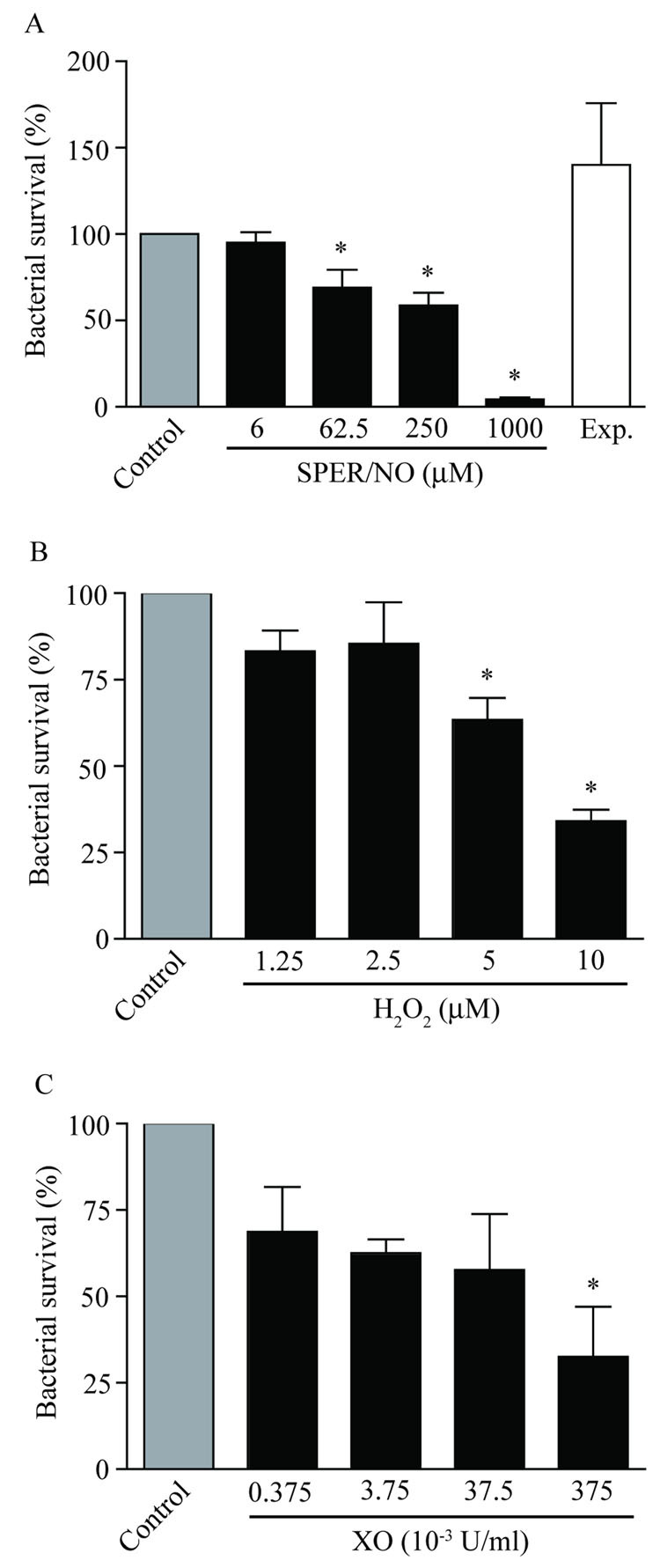
Figure 1. Dose-dependent antimicrobial activity of prototypical airway redox species.
Approximately 5,000 CFU B. bronchiseptica were exposed to A) NO (generated from SPER/NO at the listed micromolar concentrations); B) H2O2 at final µM concentrations from diluted stock; or C) O2.− (reported as xanthine oxidase concentration in U/ml). All the redox species tested displayed dose-dependent antimicrobial activity against B. bronchiseptica. Bacterial survival was determined after a 5 h exposure period (± SEM) as compared to buffer controls and are representative of at least three independent experiments. “Exp” in A indicates experiment conducted with expired SPER/NO (1000 µM). “*” indicates statistical significance relative to matched controls (P < 0.05).