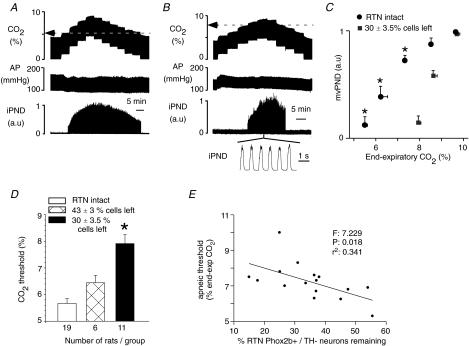
Figure 5. Effect of bilateral injections of SSP-SAP into the RTN on the central chemoreflex.
A, relationship between PND and end-expiratory CO2 in a control rat 2 weeks after bilateral injection of saline. The apnoeic threshold is 5.2%. B, same experiment in a different rat 2 weeks after bilateral treatment with 2 × 0.6 ng of SSP-SAP. The apnoeic threshold is 7.9%. PND above the apnoeic threshold appears normal. C, relationship between mvPND and end-expiratory CO2 in controls (n = 19) and in 11 rats treated bilaterally with 2 × 0.6 ng of SSP-SAP causing the destruction of 70% of the Phox2b+TH− neurons of RTN. One arbitrary unit represents the highest value of mvPND registered at steady state with end-expiratory CO2 set at 9.5–10%. * Statistical significance by RM ANOVA (P < 0.05). D, effect of graded lesions of the Phox2b+TH− neurons of the RTN on the apnoeic threshold measured as shown in A and B. * Statistically significant difference from the other two groups by ANOVA (P < 0.05). E, correlation between apnoeic threshold and percentage Phox2b+TH− neurons remaining (10 rats with 2 injections of toxin on each side and 6 rats with one injection on each side). The F, r2 and probability values of the linear regression are indicated in the figure.